Unpredictable spikes and drops in demand combined with chronic supply chain and labor shortages are accelerating the pace of digital transformation in manufacturing, starting with worker safety. Forty-eight percent of manufacturers say their progress on digital transformation initiatives has accelerated so much that it’s years ahead of what was originally anticipated, according to a KPMG study. Keeping workers safe and connected is the primary goal of most digital transformation and hiring plans, with on-site distancing & workplace safety listed as the two highest priorities.
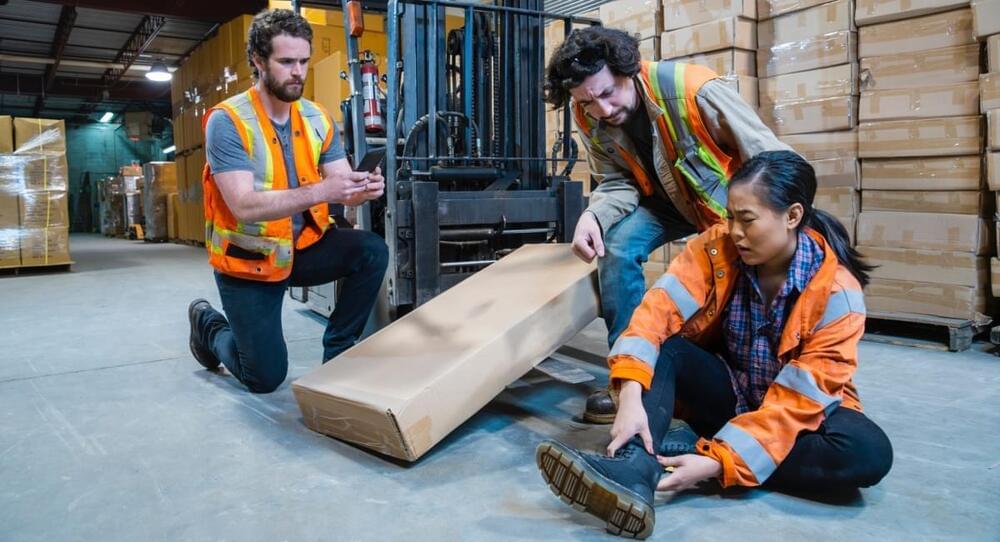
Everguard.ai, a startup based in Irvine, California, combines AI, computer vision, and sensor fusion to reduce the risk of injuries and accidents by preventing them before they happen. The company’s SENTRI360 platform proves effective in preventing workplace injuries and operational downtimes at several steel-heavy manufacturing companies, including Zekelman Industries and SeAH Besteel.
From redesigning shop floors, to meeting social distancing guidelines, and doubling their investment in training and development, worker safety now dominates manufacturing — even more so due to the pandemic. Frontline workers saved many manufacturing companies from going out of business by applying their expertise and insights in real-time, enabling entire plants to pivot and produce new products at record speed. Continued trade tensions, tariffs, and supplier shortages put more pressure on manufacturers to reshore production and have worker safety programs in place now. As manufacturing returns to the U.S., AI and computer vision are stepping up to improve worker safety.