Scientists hope the CRISPR-based therapy could treat neurodegenerative disease.

The terrorist or psychopath of the future, however, will have not just the Internet or drones—called “slaughterbots” in this video from the Future of Life Institute—but also synthetic biology, nanotechnology, and advanced AI systems at their disposal. These tools make wreaking havoc across international borders trivial, which raises the question: Will emerging technologies make the state system obsolete? It’s hard to see why not. What justifies the existence of the state, English philosopher Thomas Hobbes argued, is a “social contract.” People give up certain freedoms in exchange for state-provided security, whereby the state acts as a neutral “referee” that can intervene when people get into disputes, punish people who steal and murder, and enforce contracts signed by parties with competing interests.
The trouble is that if anyone anywhere can attack anyone anywhere else, then states will become—and are becoming—unable to satisfy their primary duty as referee.
In The Future of Violence, Benjamin Wittes and Gabriella Blum discuss a disturbing hypothetical scenario. A lone actor in Nigeria, “home to a great deal of spamming and online fraud activity,” tricks women and teenage girls into downloading malware that enables him to monitor and record their activity, for the purposes of blackmail. The real story involved a California man who the FBI eventually caught and sent to prison for six years, but if he had been elsewhere in the world he might have gotten away with it. Many countries, as Wittes and Blum note, “have neither the will nor the means to monitor cybercrime, prosecute offenders, or extradite suspects to the United States.”
Technology is, in other words, enabling criminals to target anyone anywhere and, due to democratization, increasingly at scale. Emerging bio-, nano-, and cyber-technologies are becoming more and more accessible. The political scientist Daniel Deudney has a word for what can result: “omniviolence.” The ratio of killers to killed, or “K/K ratio,” is falling. For example, computer scientist Stuart Russell has vividly described how a small group of malicious agents might engage in omniviolence: “A very, very small quadcopter, one inch in diameter can carry a one-or two-gram shaped charge,” he says. “You can order them from a drone manufacturer in China. You can program the code to say: ‘Here are thousands of photographs of the kinds of things I want to target.’ A one-gram shaped charge can punch a hole in nine millimeters of steel, so presumably you can also punch a hole in someone’s head. You can fit about three million of those in a semi-tractor-trailer. You can drive up I-95 with three trucks and have 10 million weapons attacking New York City. They don’t have to be very effective, only 5 or 10% of them have to find the target.” Manufacturers will be producing millions of these drones, available for purchase just as with guns now, Russell points out, “except millions of guns don’t matter unless you have a million soldiers. You need only three guys to write the program and launch.” In this scenario, the K/K ratio could be perhaps 3/1,000,000, assuming a 10-percent accuracy and only a single one-gram shaped charge per drone.
Will emerging technologies make the state system obsolete? It’s hard to see why not.

Washington State University researchers have made a key advance in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) that could make the highly energy-efficient and low-polluting technology a more viable alternative to gasoline combustion engines for powering cars.
Led by Ph.D. graduate Qusay Bkour and Professor Su Ha in the Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering, the researchers have developed a unique and inexpensive nanoparticle catalyst that allows the fuel cell to convert logistic liquid fuels such as gasoline to electricity without stalling out during the electrochemical process. The research, featured in the journal, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, could result in highly efficient gasoline-powered cars that produce low carbon dioxide emissions that contribute to global warming.
“People are very concerned about energy, the environment, and global warming,” said Bkour. “I’m very excited because we can have a solution to the energy problem that also reduces the emissions that cause global warming.”
The Stanford team worked with researchers at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to develop a technique called prophylactic antiviral CRISPR in human cells, or PAC-MAN. The technology disables viruses by scrambling their genetic code. The researchers developed a new way to deliver the technology into lung cells, they reported in the journal Cell.
Stanford bioengineers teamed up with researchers at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to develop a CRISPR system that neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by scrambling the virus’s genetic code. They believe the technology could prove useful for combating several types of viruses, including influenza.
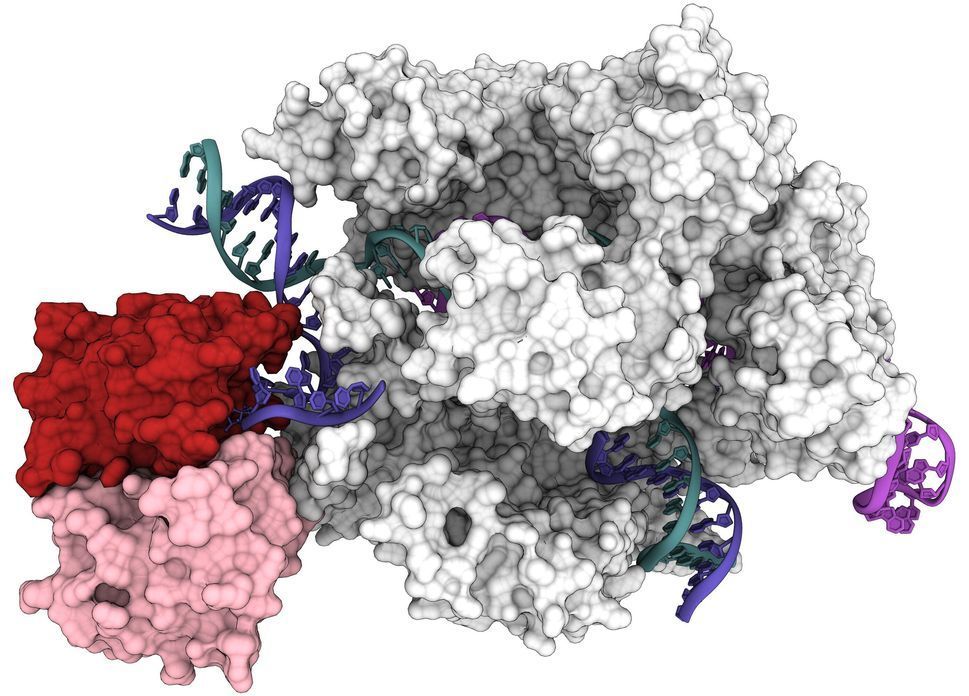
Within a mere eight years, CRISPR-Cas9 has become the go-to genome editor for both basic research and gene therapy. But CRISPR-Cas9 also has spawned other potentially powerful DNA manipulation tools that could help fix genetic mutations responsible for hereditary diseases.
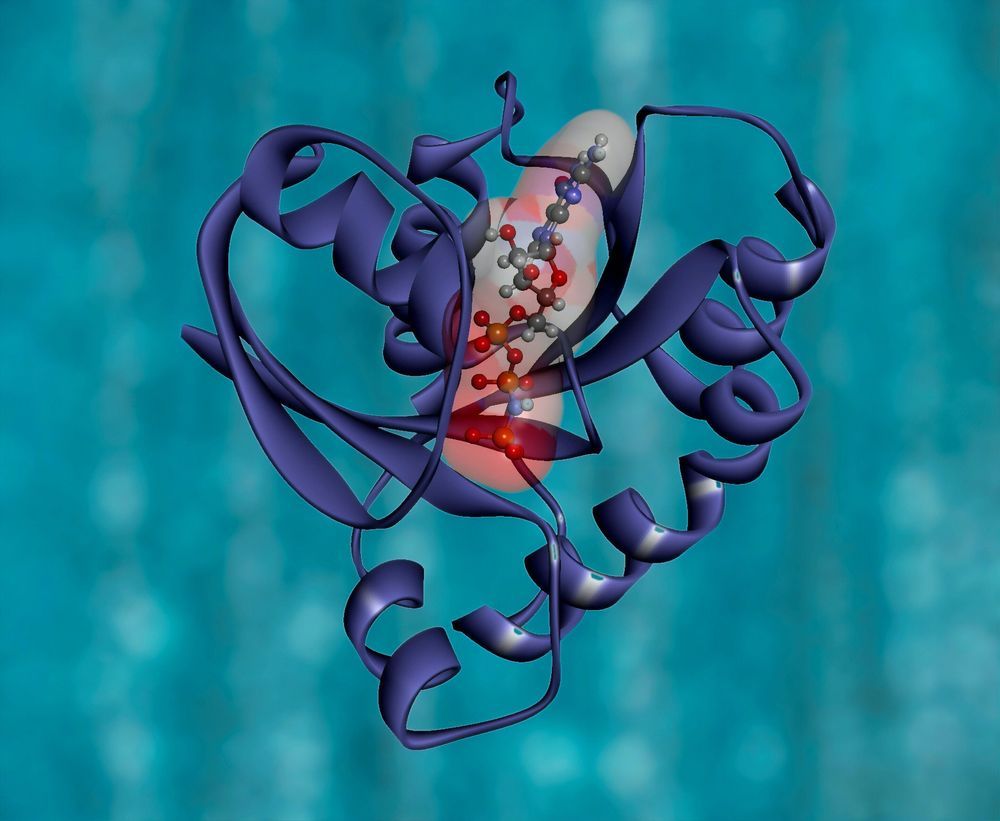
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have now obtained the first 3D structure of one of the most promising of these tools: base editors, which bind to DNA and, instead of cutting, precisely replace one nucleotide with another.
First created four years ago, base editors are already being used in attempts to correct single-nucleotide mutations in the human genome. Base editors now available could address about 60% of all known genetic diseases—potentially more than 15,000 inherited disorders—caused by a mutation in only one nucleotide.
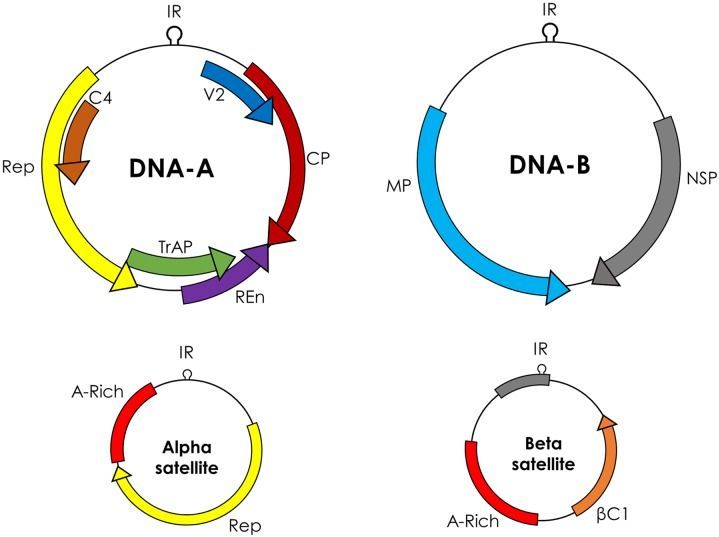
Plant viruses infect many economically important crops, including wheat, cotton, maize, cassava, and other vegetables. These viruses pose a serious threat to agriculture worldwide, as decreases in cropland area per capita may cause production to fall short of that required to feed the increasing world population. Under these circumstances, conventional strategies can fail to control rapidly evolving and emerging plant viruses. Genome-engineering strategies have recently emerged as promising tools to introduce desirable traits in many eukaryotic species, including plants. Among these genome engineering technologies, the CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats)/CRISPR-associated 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system has received special interest because of its simplicity, efficiency, and reproducibility. Recent studies have used CRISPR/Cas9 to engineer virus resistance in plants, either by directly targeting and cleaving the viral genome, or by modifying the host plant genome to introduce viral immunity. Here, we briefly describe the biology of the CRISPR/Cas9 system and plant viruses, and how different genome engineering technologies have been used to target these viruses. We further describe the main findings from recent studies of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated viral interference and discuss how these findings can be applied to improve global agriculture. We conclude by pinpointing the gaps in our knowledge and the outstanding questions regarding CRISPR/Cas9-mediated viral immunity.
Keywords: plant virus, CRISPR/Cas9, genome engineering, geminivirus, virus resistance.
In the context of the rapidly growing global population, food security has emerged as one of the major challenges facing our generation (Cheeseman, 2016). The global population has increased by 60%, but per capita production of grains has fallen worldwide in the last 20 years (Suweis et al., 2015). If the population growth rate, which is 1.13 percent per year for 20161 persists, the world population will double again within a mere 50 years, and it is estimated that food production will need to at least double till 2050 to meet demand (Suweis et al., 2015). Increases in food production per unit of land have not kept pace with increases in population and cropland area per capita has fallen by more than half since 1960 (Cheeseman, 2016).
Are you fascinated with microbiology? Have you ever thought about how to integrate your passion for research and entrepreneurship? The field of microbiology is expanding and being significantly impacted by advancements in technology. Recently, we interviewed Zack Abbott, Ph.D., who is the co-founder of ZBiotics. Zack explained his journey from studying infectious diseases to starting his own business focused on engineering bacteria for positive results. If you’ve ever wondered how you can be on the cutting edge of life sciences research, while working for yourself, read on about Zack’s experience.
1. Can you tell us a little bit about your background before entering the microbiology field?
I did my undergrad at UC Berkeley, where I double-majored in Molecular and Cell Biology and Classical History. I did not leave college thinking I would be a microbiologist. I wasn’t actually sure what I wanted to do, and so I tried out a few different jobs. Eventually, while gaining experience as a research assistant in an HIV lab at UC Davis, I realized that I would be happy with a career in infectious disease.

Summary: Tufts researchers have developed neurotransmitter-lipid hybrids that help transport therapeutic drugs and gene editing proteins across the blood-brain barrier in mice.
Source: Tufts University
Biomedical engineers at the Tufts University School of Engineering have developed tiny lipid-based nanoparticles that incorporate neurotranmitters to help carry drugs, large molecules, and even gene editing proteins across the blood-brain barrier and into the brain in mice. The innovation, published today in Science Advances, could overcome many of the current limitations encountered in delivering therapeutics into the central nervous system, and opens up the possibility of using a wide range of therapeutics that would otherwise not have access to the brain.

I am for ethical Ai. What about you?
Sophia interviews Stanford AI Researcher Tina White about how A.I. & Robotics can help stop the spread of Covid19 through contact tracing while preserving users’ privacy.
- What are you doing to stop the spread? 0:50
- What is contact tracing? How does it help stop the spread? 2:28
- How did you get the idea for your app? 2:54
- Why is privacy important to humans? 3:46.
Check out Tina’s app here: https://www.covid-watch.org/
Follow Sophia the Robot:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/realsophiarobot
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/realsophiarobot
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/realsophiar…
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/realsophi…
YouTube: https://bit.ly/2RMawys
About Hanson Robotics:
Hanson Robotics is an AI and robotics company dedicated to creating empathetic, living, intelligent machines that enrich our lives. Our innovations in AI research and development, robotics engineering, experiential design, storytelling, and material science bring robots to life as engaging characters, useful products, and evolving AI to achieve the ever-greater good for all.

Proteins are essential to the life of cells, carrying out complex tasks and catalyzing chemical reactions. Scientists and engineers have long sought to harness this power by designing artificial proteins that can perform new tasks, like treat disease, capture carbon, or harvest energy, but many of the processes designed to create such proteins are slow and complex, with a high failure rate.
In a breakthrough that could have implications across the healthcare, agriculture, and energy sectors, a team lead by researchers in the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) at the University of Chicago has developed an artificial intelligence-led process that uses big data to design new proteins.
By developing machine-learning models that can review protein information culled from genome databases, the researchers found relatively simple design rules for building artificial proteins. When the team constructed these artificial proteins in the lab, they found that they performed chemistries so well that they rivaled those found in nature.