The more crops we cultivate, the less chance our food supply wil get wiped out by a disease.
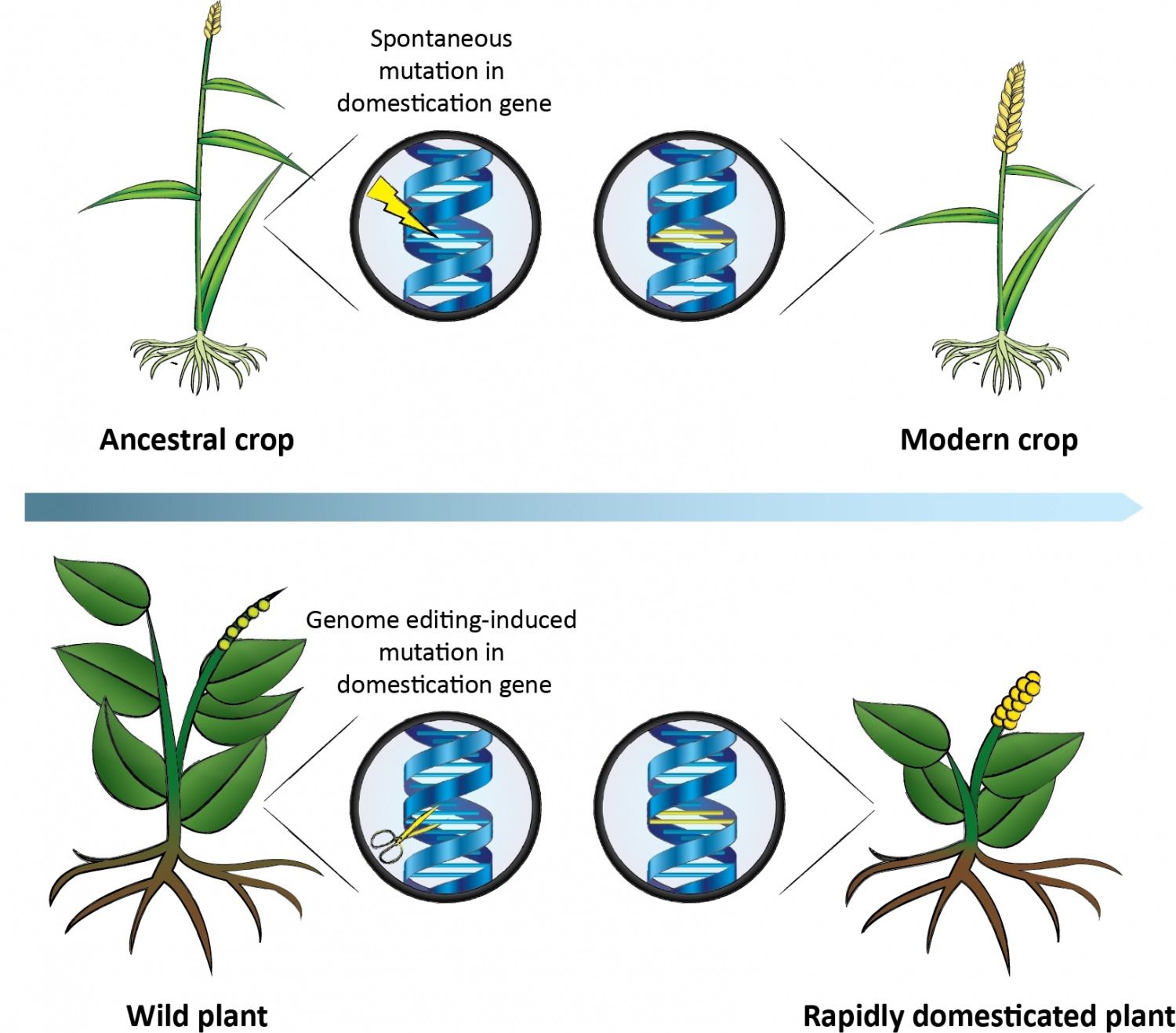
Out of the more than 300,000 plant species in existence, only three species—rice, wheat, and maize—account for most of the plant matter that humans consume, partly because in the history of agriculture, mutations arose that made these crops the easiest to harvest. But with CRISPR technology, we don’t have to wait for nature to help us domesticate plants, argue researchers at the University of Copenhagen. In a Review published March 2 in Trends in Plant Science, they describe how gene editing could make, for example, wild legumes, quinoa, or amaranth, which are already sustainable and nutritious, more farmable.
“In theory, you can now take those traits that have been selected for over thousands of years of crop domestication—such as reduced bitterness and those that facilitate easy harvest—and induce those mutations in plants that have never been cultivated,” says senior author Michael Palmgren, a botanist who heads an interdisciplinary think tank called “Plants for a Changing World” at the University of Copenhagen.
The approach has already been successful in accelerating domestication of undervalued crops using less precise gene-editing methods. For example, researchers used chemical mutagenesis to induce random mutations in weeping rice grass, an Australian wild relative of domestic rice, to make it more likely to hold onto its seeds after ripening. And in wild field cress, a type of weedy grass, scientists silenced genes with RNA interference involved with fatty acid synthesis, resulting in improved seed oil quality.