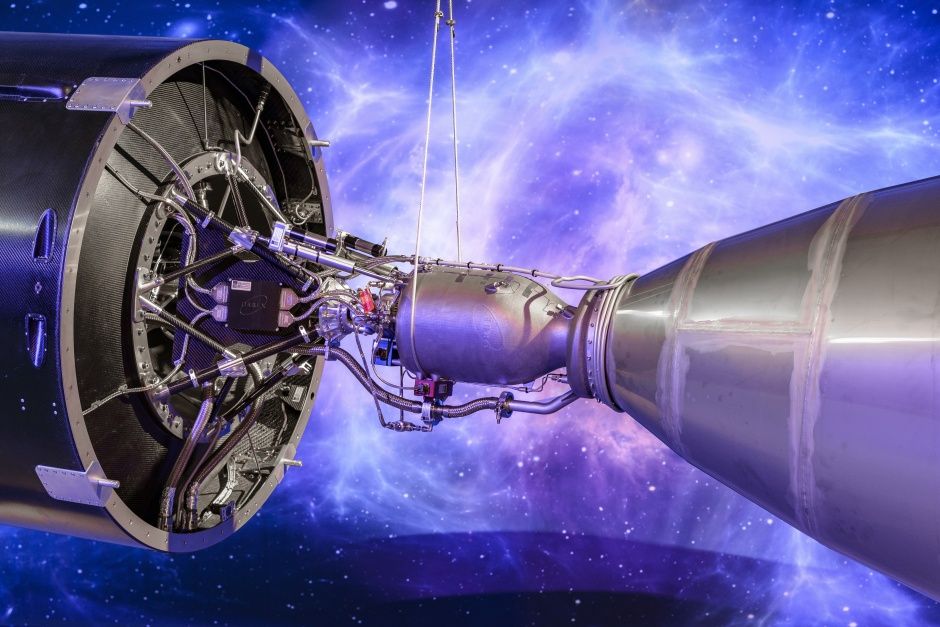
Scottish space firm Orbex has unveiled an engineering prototype of a rocket that’s at the heart of plans to develop a UK satellite launch capability.
The company, which is involved in plans to develop the UK’s first spaceport in Sutherland, Scotland unveiled the rocket at the opening of its new headquarters and rocket design facility in Forres in the Scottish Highlands.
Designed to deliver small satellites into Earth’s orbit, Orbex Prime is a two-stage rocket that’s claimed to be up to 30% lighter and 20% more efficient than any other vehicle in the small launcher category. It is also the first commercial rocket engine designed to work with bio-propane, a clean-burning, renewable fuel source that cuts carbon emissions by 90% compared to fossil hydrocarbon fuels.
Read more