In the future, you could 3D print organ replacements and biological tissues anywhere you want!
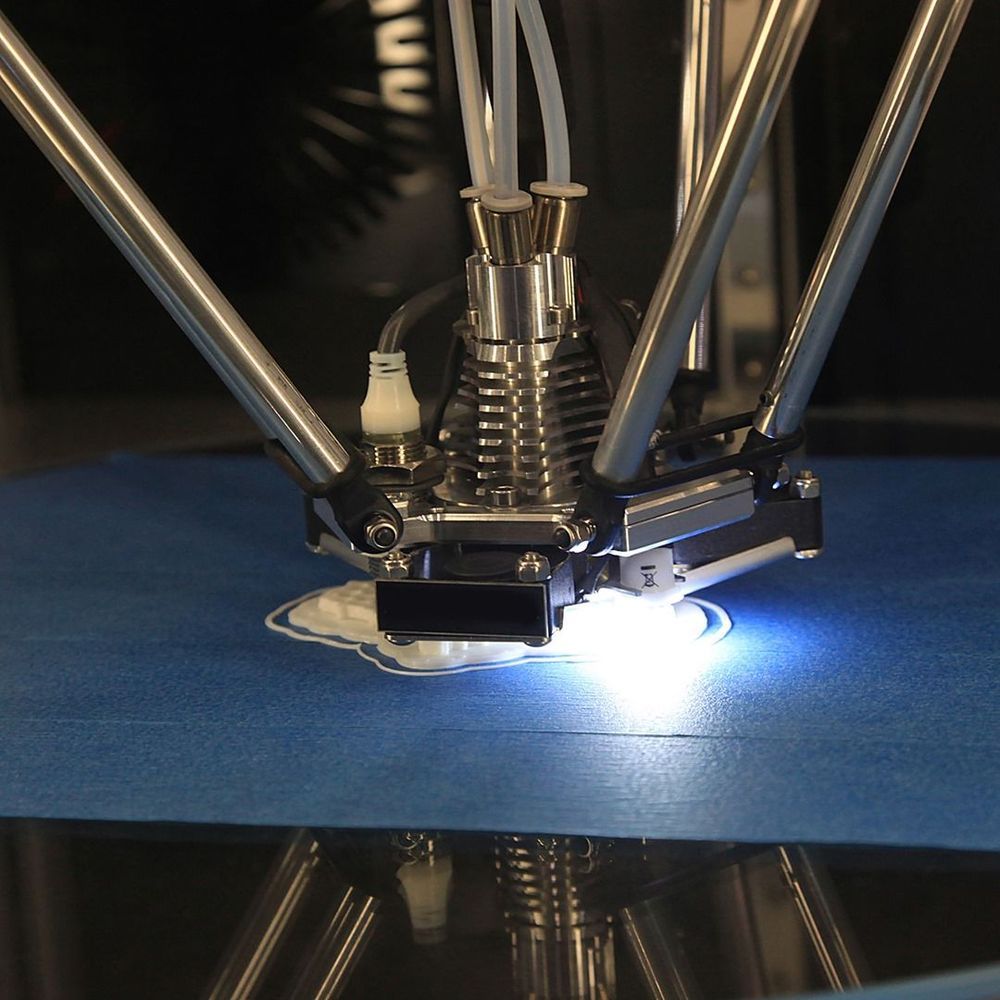

In the future, you could 3D print organ replacements and biological tissues anywhere you want!

The Michelin Vision tire concept does not need to be inflated, is specifically manufactured through 3D printing, and is biodegradable.
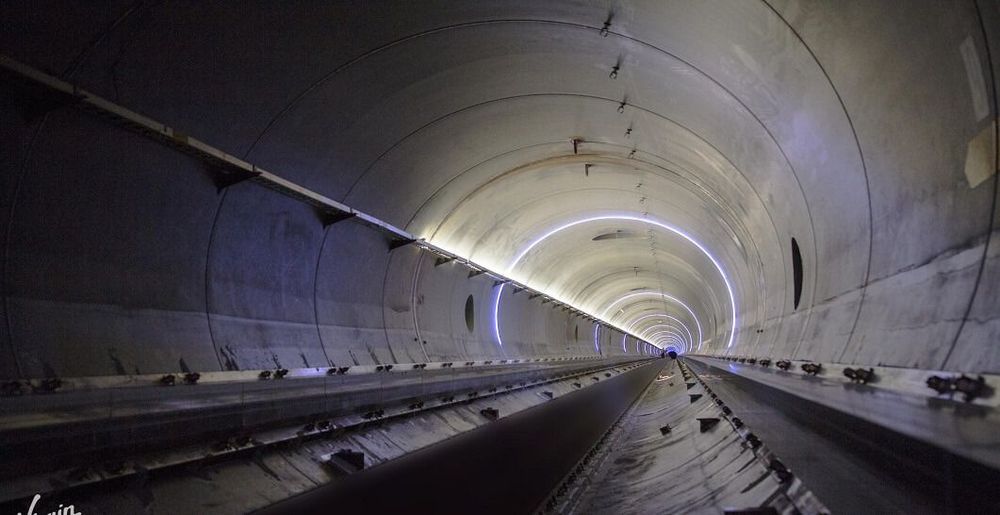



“The Hyperloop exists,” says Josh Giegel, co-founder and chief technology officer of Hyperloop One, “because of the rapid acceleration of power electronics, computational modeling, material sciences, and 3D printing.”
Thanks to these convergences, there are now ten major Hyperloop One projects—in various stages of development—spread across the globe. Chicago to DC in 35 minutes. Pune to Mumbai in 25 minutes. According to Giegel, “Hyperloop is targeting certification in 2023. By 2025, the company plans to have multiple projects under construction and running initial passenger testing.”
So think about this timetable: Autonomous car rollouts by 2020. Hyperloop certification and aerial ridesharing by 2023. By 2025—going on vacation might have a totally different meaning. Going to work most definitely will.
Get the best of Smithsonian.com by email. Keep up-to-date on:
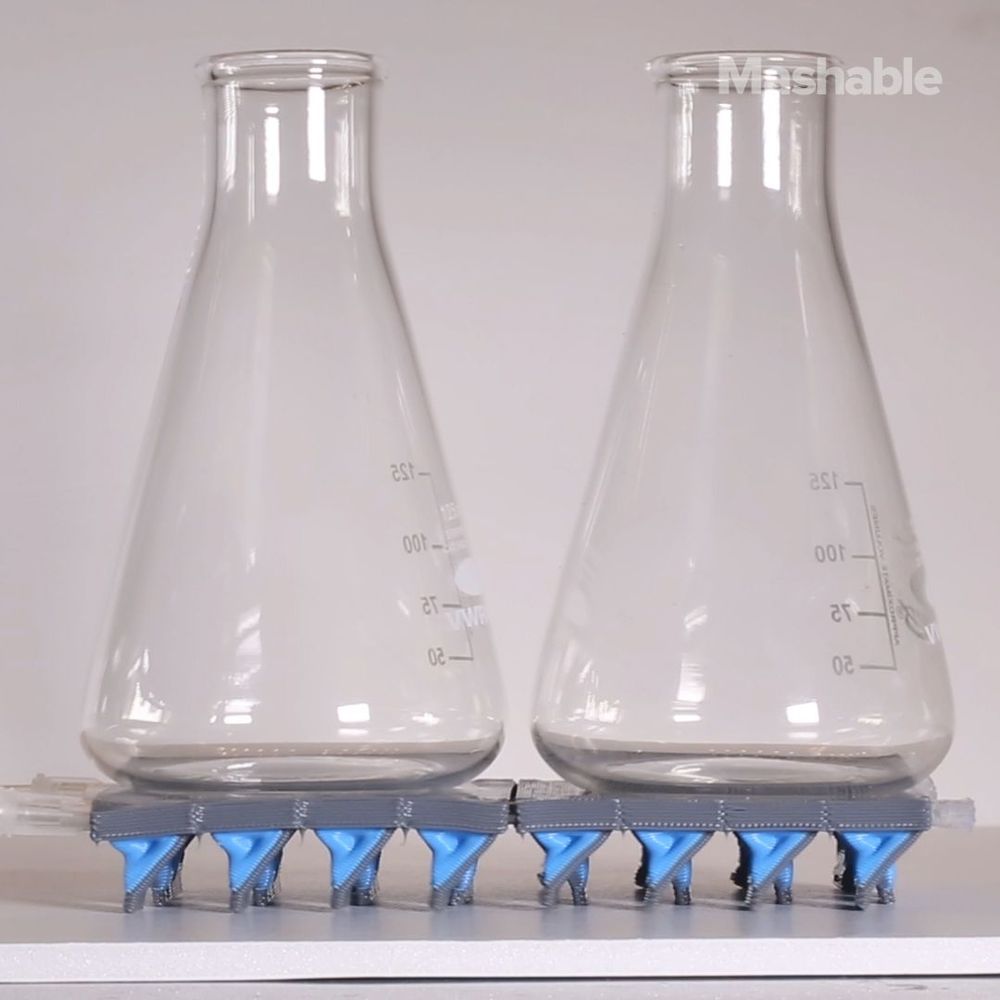

A new 3D printing technique switches between ‘inks’ so fast you can’t even see it.
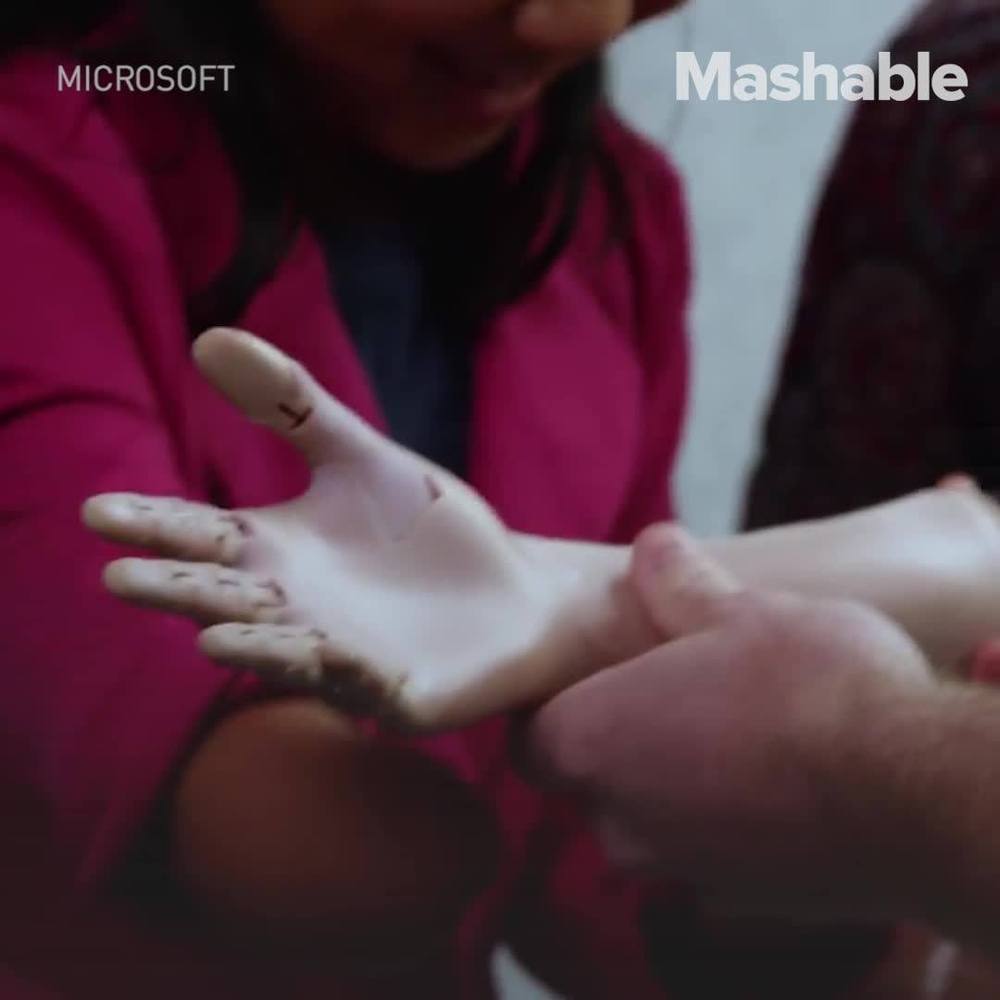

This 3D-printed robotic arm could be the most advanced and most realistic yet.

More countries coming very soon! Start your bionic journey here: http://
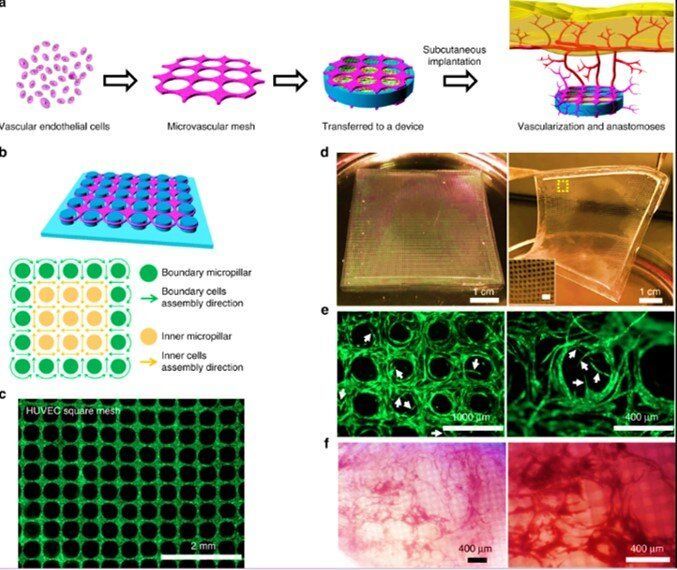
To successfully engineer cell or tissue implants, bioengineers must facilitate their metabolic requirements through vascular regeneration. However, it is challenging to develop a broad strategy for stable and functional vascularization. In a recent report on Nature Communications, Wei Song and colleagues in the interdisciplinary departments of Biological and Environmental Engineering, Medicine, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Clinical Sciences and Bioengineering in the U.S. described highly organized, biomimetic and resilient microvascular meshes. The team engineered them using controllable, anchored self-assembly methods to form microvascular meshes that are almost defect-free and transferrable to diverse substrates, for transplantation.
The scientists promoted the formation of functional blood vessels with a density as high as ~200 vessels per mm-2 within the subcutaneous space of SCID-Beige mice. They demonstrated the possibility of engineering microvascular meshes using human induced pluripotent stem-cell (iPSCs) derived endothelial cells (ECs). The technique opens a way to engineer patient-specific type 1 diabetes treatment by combining microvascular meshes for subcutaneous transplantation of rat islets in SCID-beige mice to achieve correction of chemically induced diabetes for 3 months.
Vasculature is an essential component of any organ or tissue, and vascular regeneration is critical to successfully bioengineer implants. For instance, during cell replacement therapy for type 1 diabetes (T1D), transplanted insulin producing cells rely on the vasculature to function and survive. Bioengineers often use vascular endothelial cells such as human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to spontaneously assemble into tubular structures within the extracellular matrix (ECM). But the resulting structures can be random, uncontrollable and less efficient for microvascular regeneration. Scientists have recently developed three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques to engineer controlled cellular constructs with embedded vessels. However, it remains challenging to 3D print resilient and transferrable, high-resolution, microvasculature.