A new biologically inspired battery membrane has enabled a battery with five times the capacity of the industry-standard lithium ion design to run for the thousand-plus cycles needed to power an electric car.
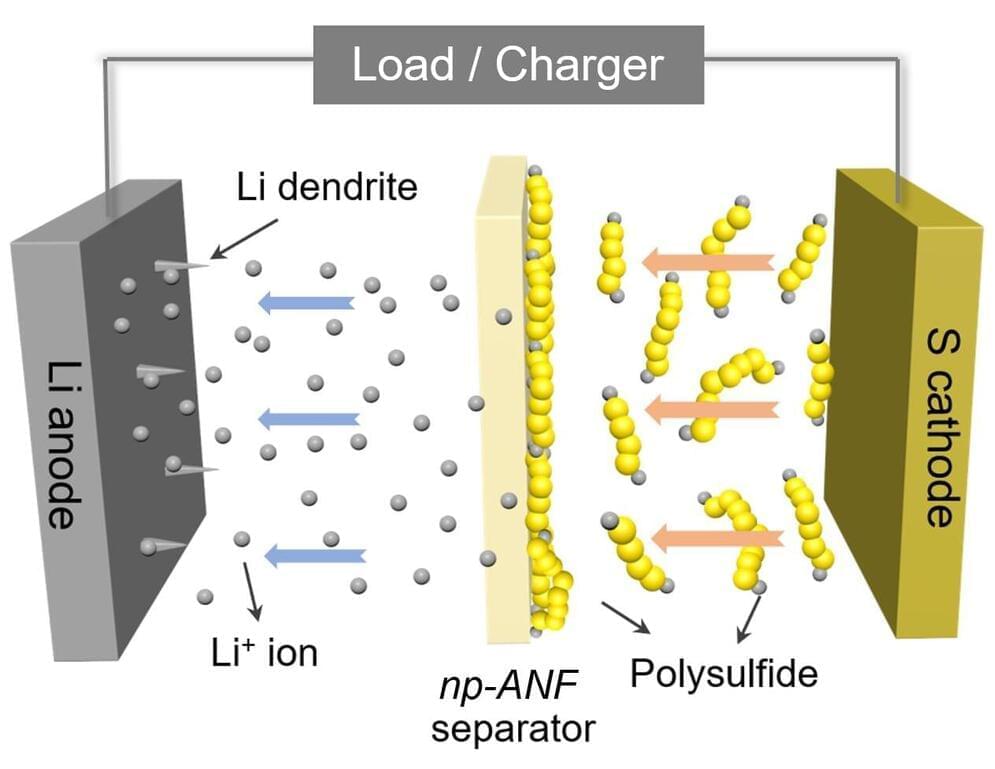
A network of aramid nanofibers, recycled from Kevlar, can enable lithium-sulfur batteries to overcome their Achilles heel of cycle life—the number of times it can be charged and discharged—a University of Michigan team has shown.
“There are a number of reports claiming several hundred cycles for lithium-sulfur batteries, but it is achieved at the expense of other parameters—capacity, charging rate, resilience and safety. The challenge nowadays is to make a battery that increases the cycling rate from the former 10 cycles to hundreds of cycles and satisfies multiple other requirements including cost,” said Nicholas Kotov, the Irving Langmuir Distinguished University Professor of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, who led the research.