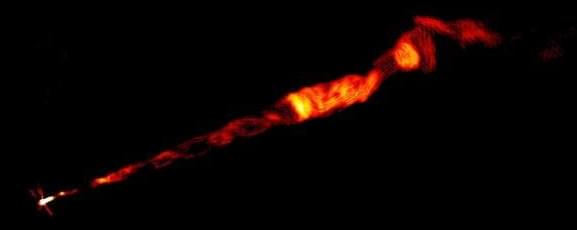
Astronomers using the National Science Foundation’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) have shown that a jet of material propelled from the core of a giant galaxy is channeled by a corkscrew-shaped magnetic field out to nearly 3,300 light-years from the galaxy’s central supermassive black hole. That is much farther than such a magnetic field previously had been detected in a galactic jet.
“By making high-quality VLA images at several different radio wavelengths of the galaxy Messier 87 (M87), we were able to reveal the 3-dimensional structure of the magnetic field in this jet for the first time,” said Alice Pasetto of the National Autonomous University of Mexico, leader of the team. “The material in this jet traces a double helix, similar to the structure of DNA,” she added.
M87 is a giant elliptical galaxy about 55 million light-years from Earth. A supermassive black hole some 6.5 billion times more massive than the Sun lurks at the center of M87. That black hole is the first one ever to be imaged—an achievement done with the world-wide Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration and announced in 2019. Earlier this year, new EHT images traced the magnetic field in the vicinity of the black hole event horizon.