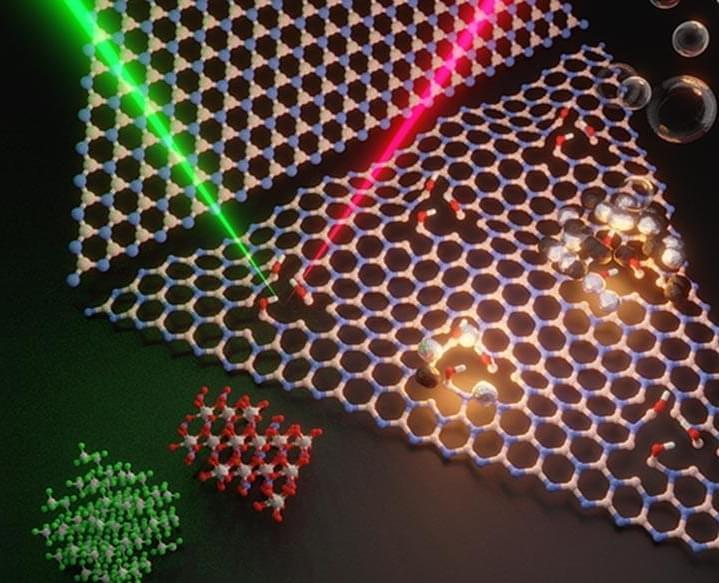
Demonstrating that a material thought to be always chemically inert, hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), can be turned chemically active holds potential for a new class of catalysts with a wide range of applications, according to an international team of researchers.
HBN is a layered material and monolayers can be exfoliated like in graphene 0, another two-dimensional material. However, there is a key difference between the two.
“While hBN shares similar structure as graphene, the strong polar bonds between the boron and nitride atoms makes hBN unlike graphene in that it is chemically inert and thermally stable at high temperature,” said Yu Lei, postdoctoral scholar in physics at Penn State and first co-author in the study published in Materials Today.