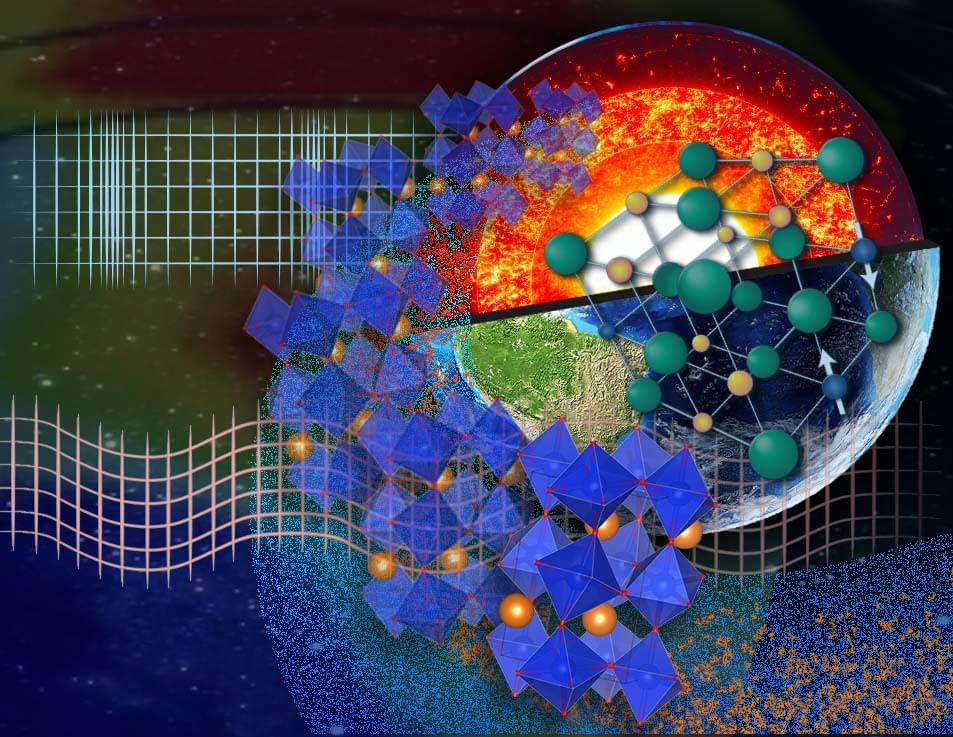
Multidisciplinary team of materials physicists and geophysicists combine theoretical predictions, simulations, and seismic tomography to find spin transition in the Earth’s mantle.
The interior of the Earth is a mystery, especially at greater depths (660 km). Researchers only have seismic tomographic images of this region and, to interpret them, they need to calculate seismic (acoustic) velocities in minerals at high pressures and temperatures. With those calculations, they can create 3D velocity maps and figure out the mineralogy and temperature of the observed regions. When a phase transition occurs in a mineral, such as a crystal structure change under pressure, scientists observe a velocity change, usually a sharp seismic velocity discontinuity.
In 2,003 scientists observed in a lab a novel type of phase change in minerals — a spin change in iron in ferropericlase, the second most abundant component of the Earth’s lower mantle. A spin change, or spin crossover, can happen in minerals like ferropericlase under an external stimulus, such as pressure or temperature. Over the next few years, experimental and theoretical groups confirmed this phase change in both ferropericlase and bridgmanite, the most abundant phase of the lower mantle. But no one was quite sure why or where this was happening.