What’s exciting about our findings is that we have identified a molecular pathway that is activated in normal acute wounds in humans, and altered in diabetic wounds in mice,” said Ghaidaa Kashgari, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in the UCI School of Medicine Department of Medicine. “This finding strongly indicates clinical relevance and may improve our understanding of wound healing biology and could lead to new therapies.
A University of California, Irvine-led study identifies a new molecular pathway that promotes the healing of wounds in the skin. Titled “GRHL3 activates FSCN1 to relax cell-cell adhesions between migrating keratinocytes during wound reepithelialization,” the study was published today in JCI Insight.
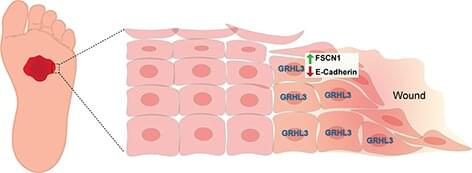
The molecular pathway identified is controlled by an evolutionary conserved gene called a Grainyhead like 3 (GRHL3), which is a gene required for mammalian development. Without this gene, several abnormalities may occur, including spina bifida, defective epidermal barrier, defective eyelid closure and soft-tissue syndactyly, a condition in which children are born with fused or webbed fingers.
The study reveals how during wound healing, GRHL3 works to activate a protein coding gene called Fascin Actin-Bundling Protein 1 (Fscn1) to loosen the adhesion between wounded skin cells so they can migrate efficiently to close the wound. Researchers also found that alterations in this process may result in chronic, non-healing wounds, such as diabetic ulcers that affect millions of patients every year.