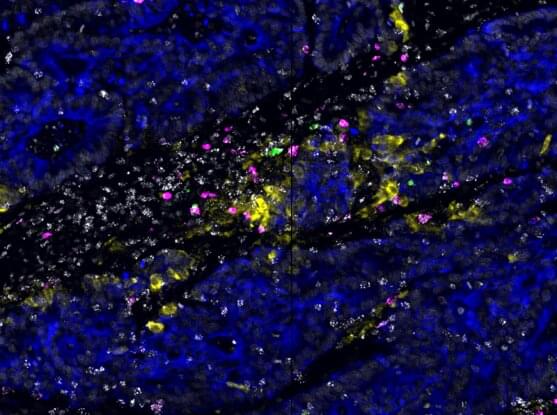
A tumor in the human body is like a city at war, bustling with cancer cells, immune cells, blood vessels, signaling molecules and surrounding tissue. A simple census of these players will provide some basic information on their battle, but won’t tell you their organization or strategy.
A team of researchers has gained new insight into this organization. They have discovered that immune cells in some human colorectal tumors gather together in clusters, like soldiers mobilizing in formation. By using a unique combination of single-cell profiling and imaging technologies, along with newly developed data analysis approaches, the scientists found a level of spatial organization of cells not observed before in tumors.
The findings, published in Cell, point to networks of interacting immune cells in certain types of colorectal tumors that tend to be more readily “seen” by the immune system. This suggests that cancers containing these hubs may be more likely to respond to cancer drugs called immunotherapies, which spur the immune system to kill cancer cells. The scientists, from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Massachusetts General Hospital, MIT, the Evergrande Center for Immunologic Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, say the study could shed light on how to make other tumors more responsive to such treatments.