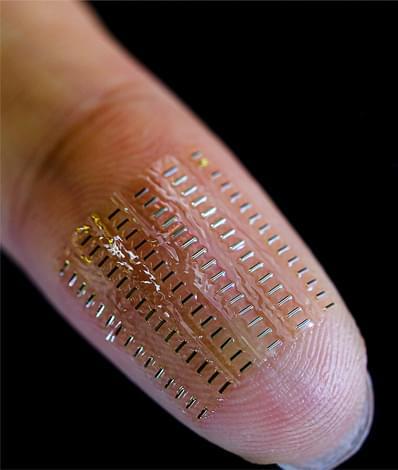
Devices in the submillimetre range – so-called “nano-supercapacitors” – allow the shrinkage of electronic components to tiny dimensions. However, they are difficult to produce and do not usually incorporate biocompatible materials. Corrosive electrolytes, for example, can quickly discharge themselves in the event of defects and contamination.
So-called “biosupercapacitors” (BSCs) offer a solution. These have two outstanding properties: full biocompatibility, which means they can be used in body fluids such as blood, and compensation for self-discharge behaviours through bio-electrochemical reactions. In other words, they can actually benefit from the body’s own reactions. This is because, in addition to typical charge storage reactions of a supercapacitor, redox enzymatic reactions and living cells naturally present in the blood can increase the performance of a device by 40%.
Shrinking these devices down to submillimetre sizes, while maintaining full biocompatibility, has been enormously challenging. Now, scientists have created a prototype that combines both essential properties.