Physics-informed machine learning might help verify microchips.
Physicists love recreating the world in software. A simulation lets you explore many versions of reality to find patterns or to test possibilities. But if you want one that’s realistic down to individual atoms and electrons, you run out of computing juice pretty quickly.
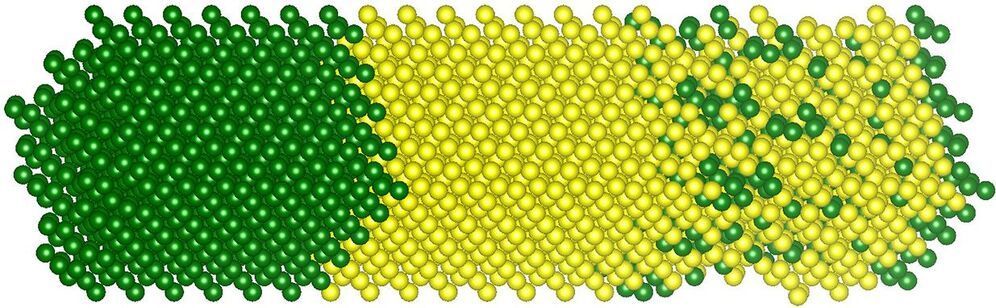
Machine-learning models can approximate detailed simulations, but often require lots of expensive training data. A new method shows that physicists can lend their expertise to machine-learning algorithms, helping them train on a few small simulations consisting of a few atoms, then predict the behavior of system with hundreds of atoms. In the future, similar techniques might even characterize microchips with billions of atoms, predicting failures before they occur.
The researchers started with simulated units of 16 silicon and germanium atoms, two elements often used to make microchips. They employed high-performance computers to calculate the quantum-mechanical interactions between the atoms’ electrons. Given a certain arrangement of atoms, the simulation generated unit-level characteristics such as its energy bands, the energy levels available to its electrons. But “you realize that there is a big gap between the toy models that we can study using a first-principles approach and realistic structures,” says Sanghamitra Neogi, a physicist at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and the paper’s senior author. Could she and her co-author, Artem Pimachev, bridge the gap using machine learning?