Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory engineers have designed a new kind of laser-driven semiconductor switch that can theoretically achieve higher speeds at higher voltages than existing photoconductive devices. If the device could be realized, it could be miniaturized and incorporated into satellites to enable communication systems beyond 5G, potentially transferring more data at a faster rate and over longer distances, according to researchers. Credit: LLNL
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) engineers have designed a new kind of laser-driven semiconductor switch that can theoretically achieve higher speeds at higher voltages than existing photoconductive devices. The development of such a device could enable next-generation satellite communication systems capable of transferring more data at a faster rate, and over longer distances, according to the research team.
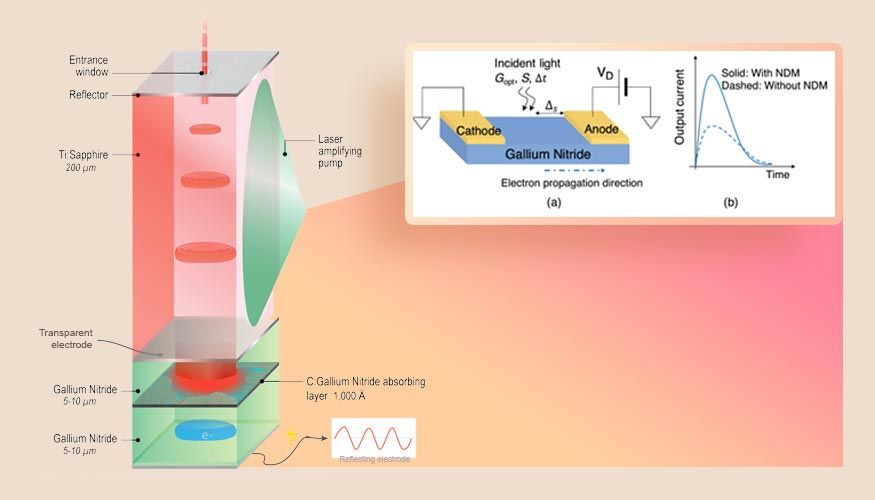
Scientists at LLNL and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) reported on the design and simulation of the novel photoconductive device in a paper published in the IEEE Journal of the Electron Devices Society. The device utilizes a high-powered laser to generate an electron charge cloud in the base material gallium nitride while under extreme electric fields.