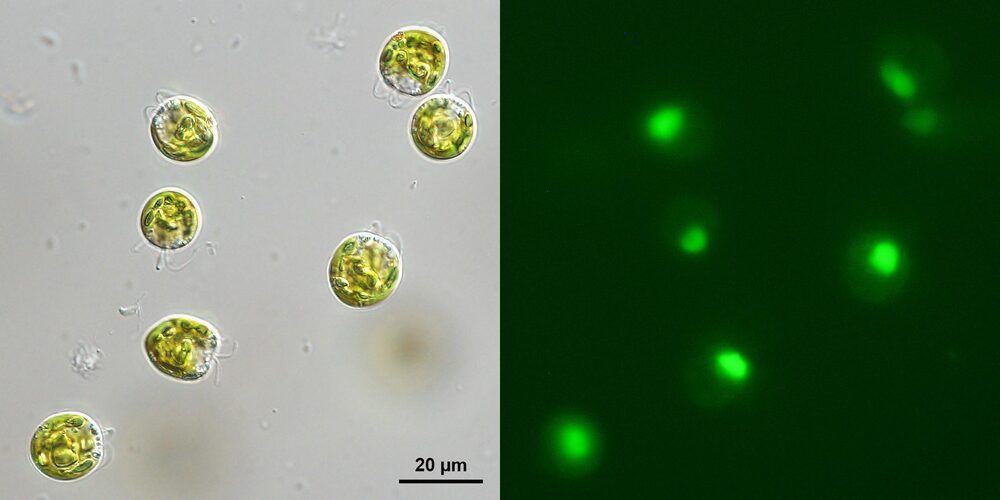
New study points to potential widespread phagocytosis among green algae, suggests improved methodology in environmental microbiology.
New research suggests that the ability of green algae to eat bacteria is likely much more widespread than previously thought, a finding that could be crucial to environmental and climate science. The work, led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History, Columbia University, and the University of Arizona, found that five strains of single-celled green algae consume bacteria when they are “hungry,” and only when those bacteria are alive. The study is published today in The ISME Journal.
“Traditionally, we think of green algae as being purely photosynthetic organisms, producing their food by soaking in sunlight,” said Eunsoo Kim, an associate curator at the American Museum of Natural History and one of the study’s corresponding authors. “But we’ve come to understand that there are potentially a number of species of green algae that also can eat bacteria when the conditions are right. And we’ve also found out just how finicky they are as eaters.”