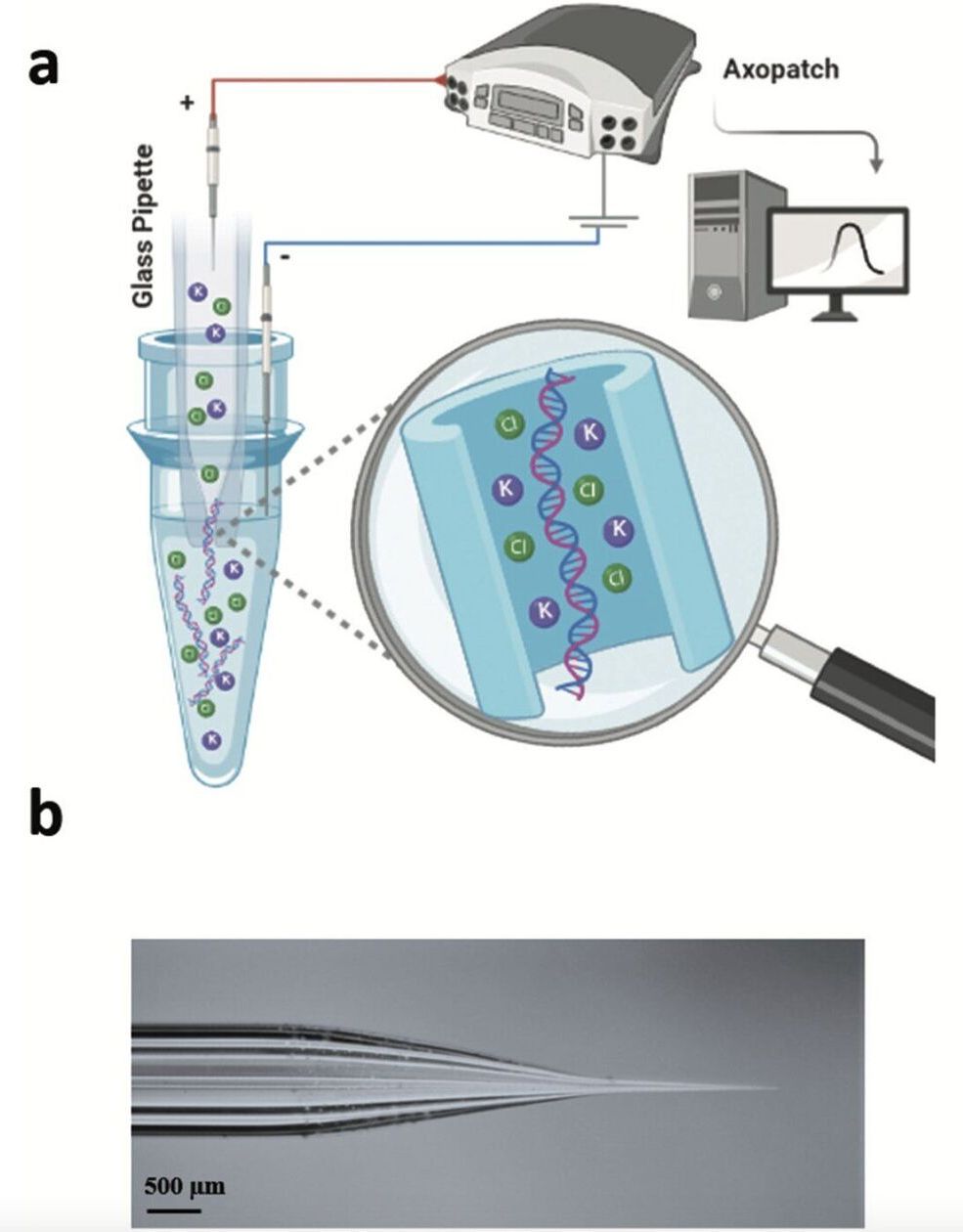
Research led by UC Riverside is making it easier to detect and capture DNA from fluid samples such as blood using a tiny glass tube and electric current. The technique, described in the journal Nanoscale, can also improve cancer diagnosis in the future.
DNA, a double-stranded, electrically charged molecule that contains all the information an organism needs to create and organize the building blocks of life, is tightly folded within the cell nucleus. Extracting the DNA from a single cell is time consuming and impractical for many medical and scientific purposes. Fortunately, as cells die naturally, their membranes burst, releasing the contents, including DNA. This means that a blood sample, for example, contains many strands of free-floating DNA that should, in theory, be easier to identify and extract in quantity.