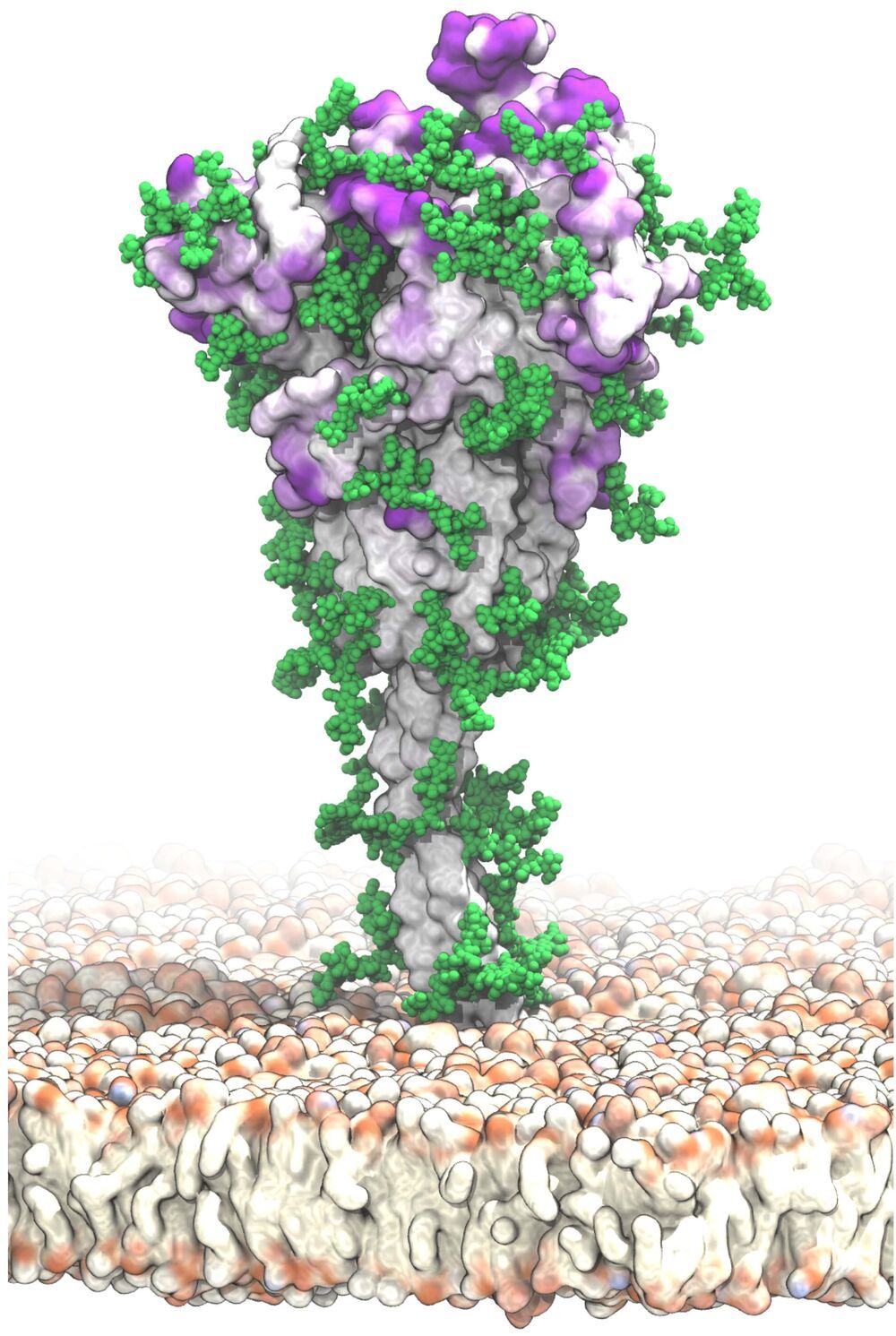
A new, detailed model of the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reveals previously unknown vulnerabilities that could inform development of vaccines. Mateusz Sikora of the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt, Germany, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
SARS-CoV-2 is the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. A key feature of SARS-CoV-2 is its spike protein, which extends from its surface and enables it to target and infect human cells. Extensive research has resulted in detailed static models of the spike protein, but these models do not capture the flexibility of the spike protein itself nor the movements of protective glycans—chains of sugar molecules—that coat it.
To support vaccine development, Sikora and colleagues aimed to identify novel potential target sites on the surface of the spike protein. To do so, they developed molecular dynamics simulations that capture the complete structure of the spike protein and its motions in a realistic environment.