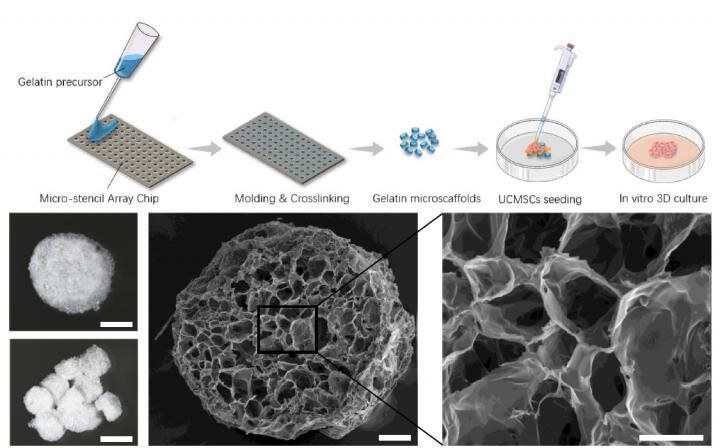
A 3D biomaterial scaffold design to slowly release stem cells ensures that implanted stem cells stick around to relieve pain and reverse arthritis in mice knee joints. This reduces the use of stem cells by 90%, thus avoiding the challenge of redness, swelling and scar tissue that can arise from large doses of such stem cells, and potentially opening a path to reversal of osteoarthritis in humans for the first time.
The results were published in the Chemical Engineering Journal on February 25.
There is currently no treatment that can reverse the course of osteoarthritis, and our sole options are to try to relieve pain. Stem cell therapy potentially offers hope and has been shown to alienate the disease, but a ‘goldilocks’ dose of stem cells remains out of reach. Too much of a dose of stem cells and the subject suffers redness, swelling and scar tissue. Too little and the therapy is only successful for a limited period due to gradual cell loss.