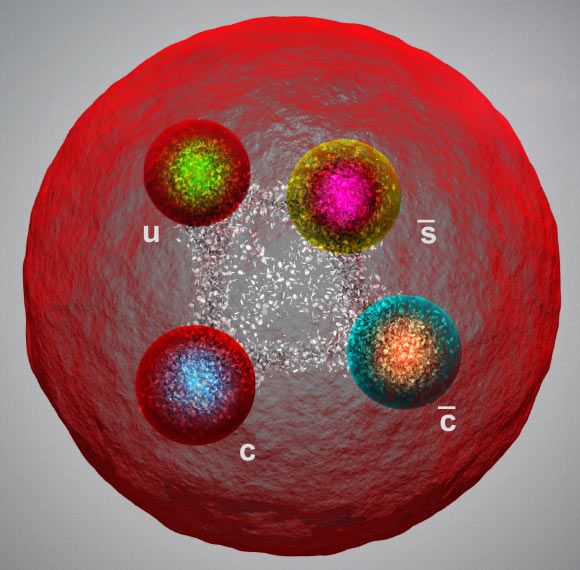
Physicists from the LHCb Collaboration at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) have observed four new exotic particles: Zcs (4000)+, Zcs (4220)+, X(4685), and X(4630). The new results provide grist for the mill of theorists seeking to explain the nature of tetraquark binding mechanisms.
“Hadrons discovered in the 1950-60s, the pioneering years in particle physics history, were called elementary particles till their structure was finally understood in the framework of quark model,” the LHCb physicists said.