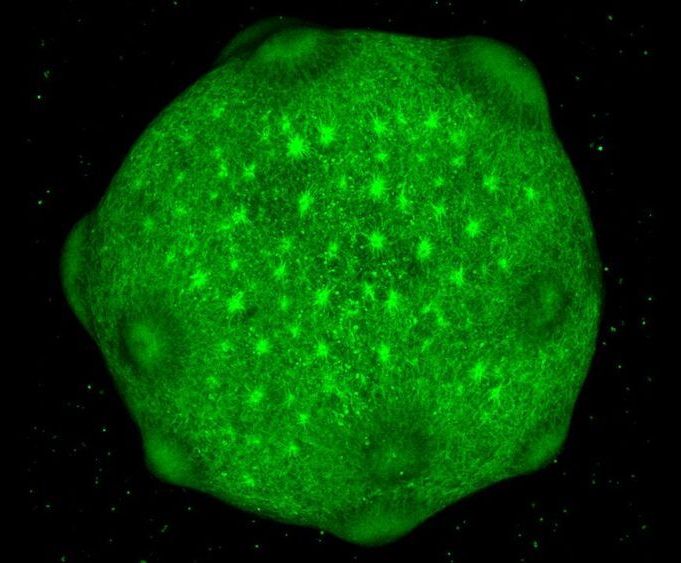
Stanford University neurobiologist Sergiu Pașca has been making brain organoids for about 10 years, and his team has learned that some of these tissue blobs can thrive in a dish for years. In the new study, they teamed up with neurogeneticist Daniel Geschwind and colleagues at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), to analyze how the blobs changed over their life spans…
…They noticed that when an organoid reached 250 to 300 days old—roughly 9 months—its gene expression shifted to more closely resemble that of cells from human brains soon after birth. The cells’ patterns of methylation—chemical tags that can affix to DNA and influence gene activity—also corresponded to increasingly mature human brain cells as the organoids aged, the team reports today in Nature Neuroscience.
Organoids develop genetic signatures of postnatal brains, possibly broadening their use as disease models.