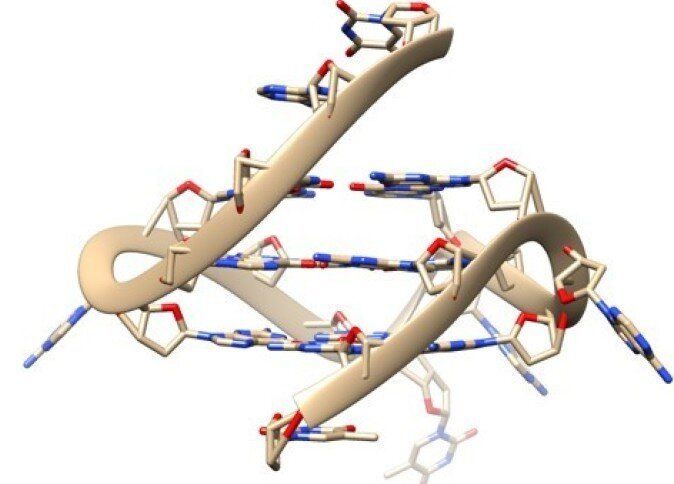
New probes allow scientists to see four-stranded DNA interacting with molecules inside living human cells, unraveling its role in cellular processes.
DNA usually forms the classic double helix shape of two strands wound around each other. While DNA can form some more exotic shapes in test tubes, few are seen in real living cells.
However, four-stranded DNA, known as G-quadruplex, has recently been seen forming naturally in human cells. Now, in new research published today in Nature Communications, a team led by Imperial College London scientists have created new probes that can see how G-quadruplexes are interacting with other molecules inside living cells.