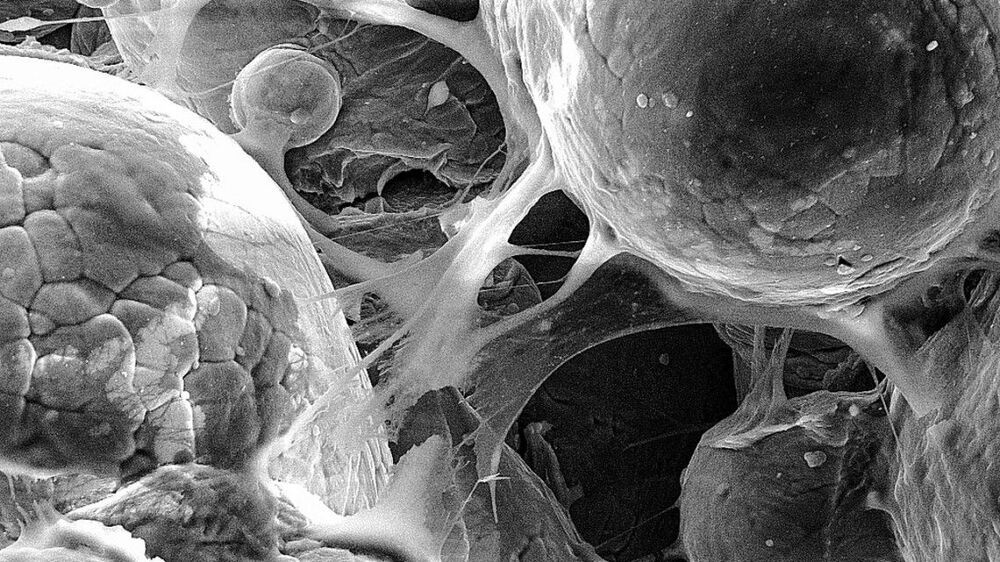
Engineers at Cornell University have developed a new technique for 3D printing metallic objects – and it involves blasting titanium particles at supersonic speeds. The resulting metals are very porous, which makes them particularly useful for biomedical objects like implants and replacement joints.
Traditional 3D printing involves a nozzle depositing plastic, hydrogels, living cells or other materials layer by layer to build up an object. Metal parts and objects are usually 3D printed in other ways, such as firing a laser at a bed of metal powder to selectively melt sections into the desired shape, or firing metal powder at high speeds at a substrate to fuse the particles together.
The latter method is known as “cold spray,” and the new technique expands on that base. The Cornell team blasted titanium alloy particles, each measuring between 45 and 106 microns wide, at speeds up to 600 m (1,969 ft) per second (for reference, the speed of sound in air is around 340 m (1,115 ft) per second). The team calculated this as the ideal speed – any faster, and the particles would disintegrate too much on impact to bond to each other.