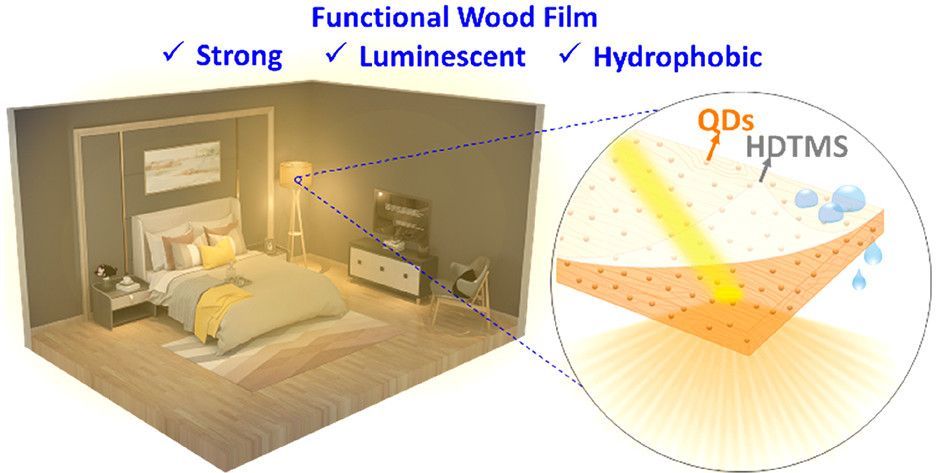
Most materials used for optical lighting applications need to produce a uniform illumination and require high mechanical and hydrophobic properties. However, they are rarely eco-friendly. Herein, a bio-based, polymer matrix-free, luminescent, and hydrophobic film with excellent mechanical properties for optical lighting purposes is demonstrated. A template is prepared by turning a wood veneer into porous scaffold from which most of the lignin and half of the hemicelluloses are removed. The infiltration of quantum dots (CdSe/ZnS) into the porous template prior to densification resulted in almost uniform luminescence (isotropic light scattering) and could be extended to various quantum dot particles, generating different light colors. In a subsequent step, the luminescent wood film is coated with hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (HDTMS) via chemical vapor deposition. The presence of the quantum dots coupled with the HDTMS coating renders the film hydrophobic (water contact angle ≈ 140°). This top-down process strongly eliminates lumen cavities and preserves the orientation of the original cellulose fibrils to create luminescent and polymer matrix-free films with high modulus and strength in the direction of fibers. The proposed optical lighting material could be attractive for interior designs (e.g., lamps and laminated cover panels), photonics, and laser devices.