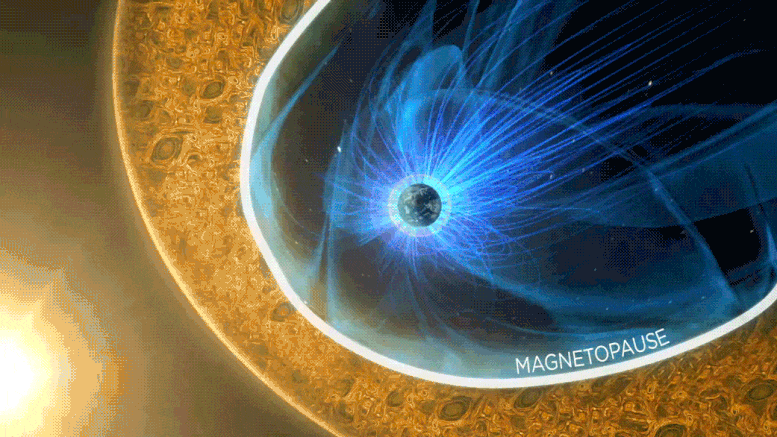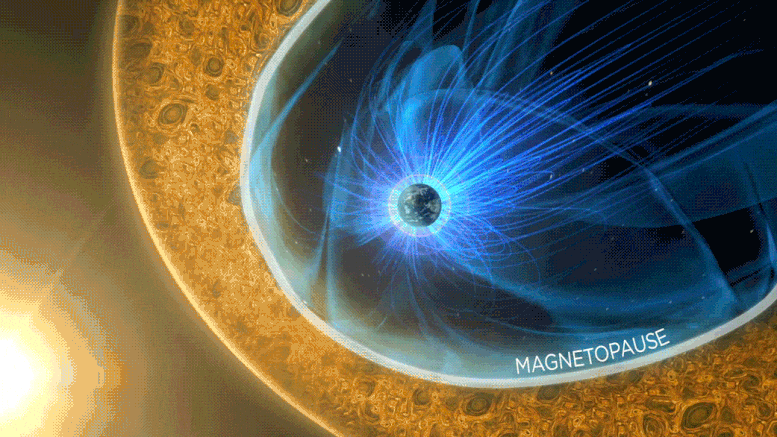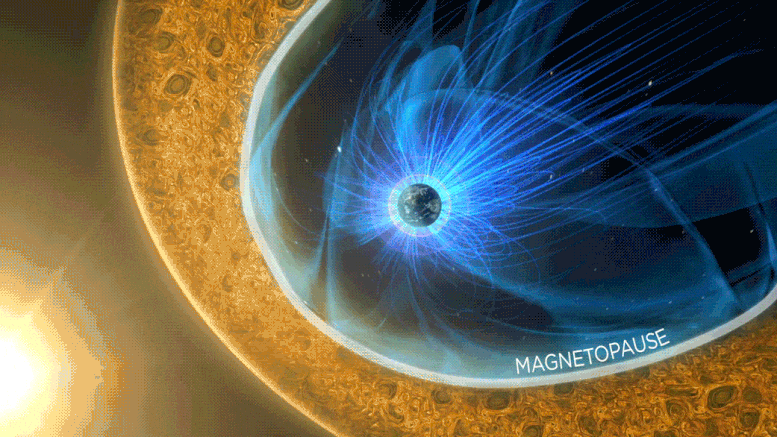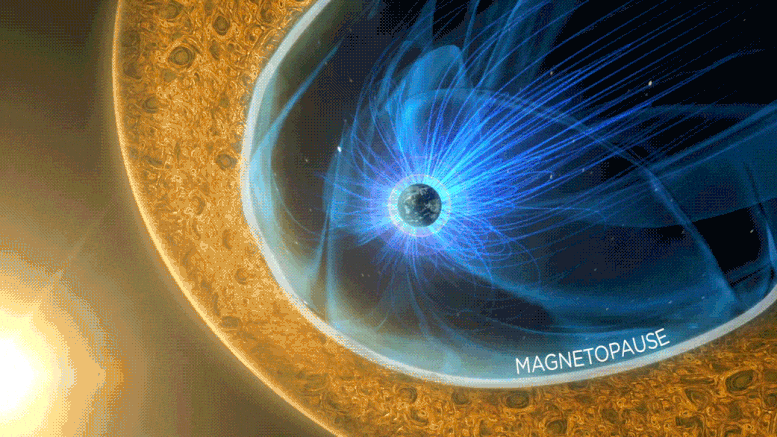
An alert pops up in your email: The latest spacecraft observations are ready. You now have 24 hours to scour 84 hours-worth of data, selecting the most promising split-second moments you can find. The data points you choose, depending on how you rank them, will download from the spacecraft in the highest possible resolution; researchers may spend months analyzing them. Everything else will be overwritten like it was never collected at all.
These are the stakes facing the Scientist in the Loop, one of the most important roles on the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, mission team. Seventy-three volunteers share the responsibility, working weeklong shifts at a time to ensure the very best data makes it to the ground. It takes a keen and meticulous eye, which is why it’s always been left to a carefully-trained human – at least until now.
A paper published recently in Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences describes the first artificial intelligence algorithm to lend the Scientist in the Loop a (virtual) hand.