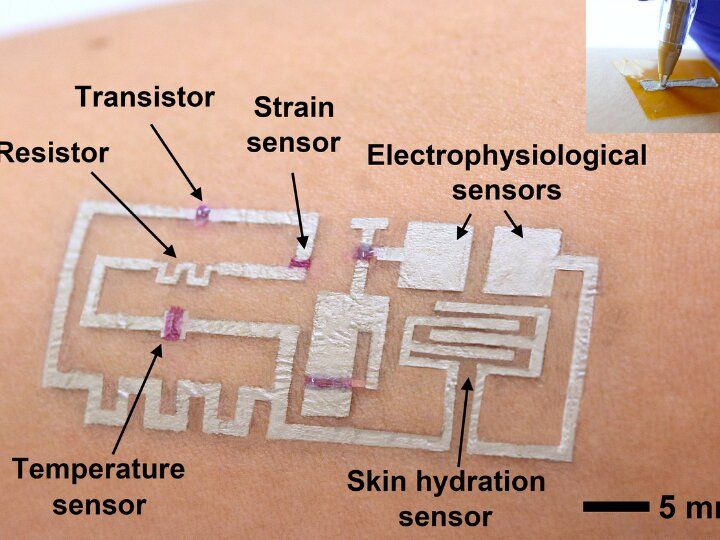
A team of researchers led by Cunjiang Yu, Bill D. Cook Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Houston, has developed a new form of electronics known as “drawn-on-skin electronics,” allowing multifunctional sensors and circuits to be drawn on the skin with an ink pen.
The advance, the researchers report in Nature Communications, allows for the collection of more precise, motion artifact-free health data, solving the long-standing problem of collecting precise biological data through a wearable device when the subject is in motion.
The imprecision may not be important when your FitBit registers 4,000 steps instead of 4,200, but sensors designed to check heart function, temperature and other physical signals must be accurate if they are to be used for diagnostics and treatment.