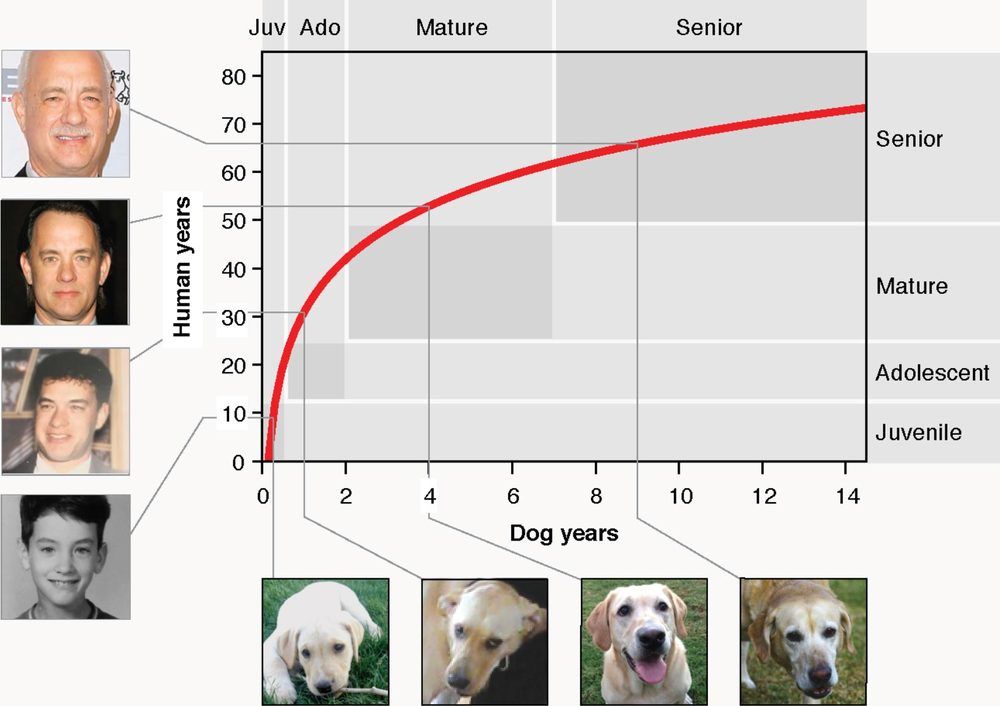
If there’s one myth that has persisted through the years without much evidence, it’s this: multiply your dog’s age by seven to calculate how old they are in “human years.” In other words, the old adage says, a four-year-old dog is similar in physiological age to a 28-year-old person.
But a new study by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine throws that out the window. Instead, they created a formula that more accurately compares the ages of humans and dogs. The formula is based on the changing patterns of methyl groups in dog and human genomes — how many of these chemical tags and where they’re located — as they age. Since the two species don’t age at the same rate over their lifespans, it turns out it’s not a perfectly linear comparison, as the 1:7 years rule-of-thumb would suggest.