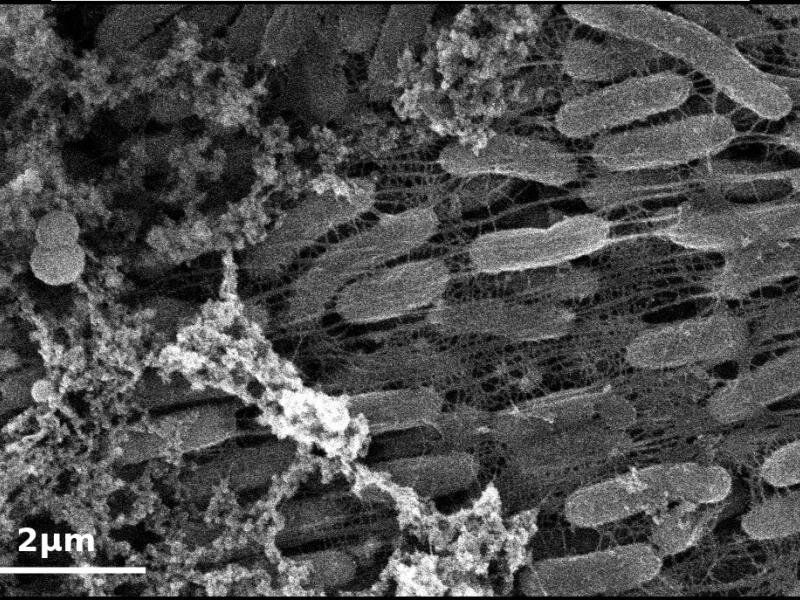
When the Shewanella oneidensis bacterium “breathes” in certain metal and sulfur compounds anaerobically, the way an aerobic organism would process oxygen, it produces materials that could be used to enhance electronics, electrochemical energy storage, and drug-delivery devices.
The ability of this bacterium to produce molybdenum disulfide—a material that is able to transfer electrons easily, like graphene—is the focus of research published in Biointerphases by a team of engineers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
“This has some serious potential if we can understand this process and control aspects of how the bacteria are making these and other materials,” said Shayla Sawyer, an associate professor of electrical, computer, and systems engineering at Rensselaer.