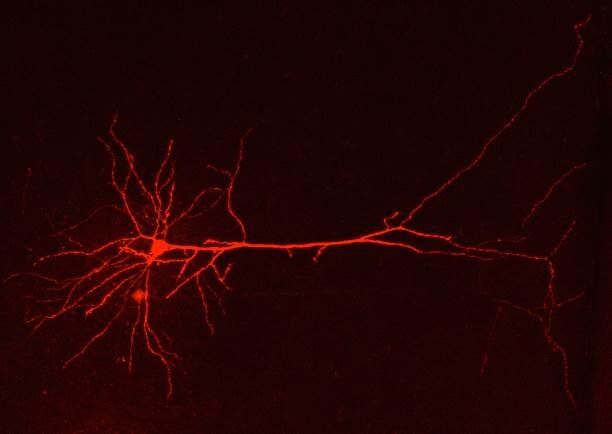
“Despite their abundance, astrocytes have been relatively overlooked by neuroscientists,” says Mirko Santello, last author of the study. Yet these cells are extremely important to clear transmitters released by neurons. In their study the researchers were able to show that in familial migraine the astrocytes cannot remove excessive transmitters released by neurons. “The impairment in astrocytic glutamate uptake in the cingulate cortex strongly enhances cortical dendritic excitability and thus enhances firing of the neurons,” Santello says…
Migraine is a complicated disorder that affects part of the nervous system. “Our results provide a clear example of how astrocyte dysfunction produced by a genetic defect affects neuronal activity and sensitivity to head pain triggers,” explains Mirko Santello. The findings help to better understand migraine pathophysiology and suggest that the cingulate cortex may represent a critical hub in the disease. The demonstration of the link between dysfunction of astrocytes in the cingulate cortex and familial migraine could help in devising new migraine treatment strategies.
Neuroscientists of the University of Zurich shed a new light on the mechanisms responsible for familial migraine: They show that a genetic dysfunction in specific brain cells of the cingulate cortex area strongly influences head pain occurrence.