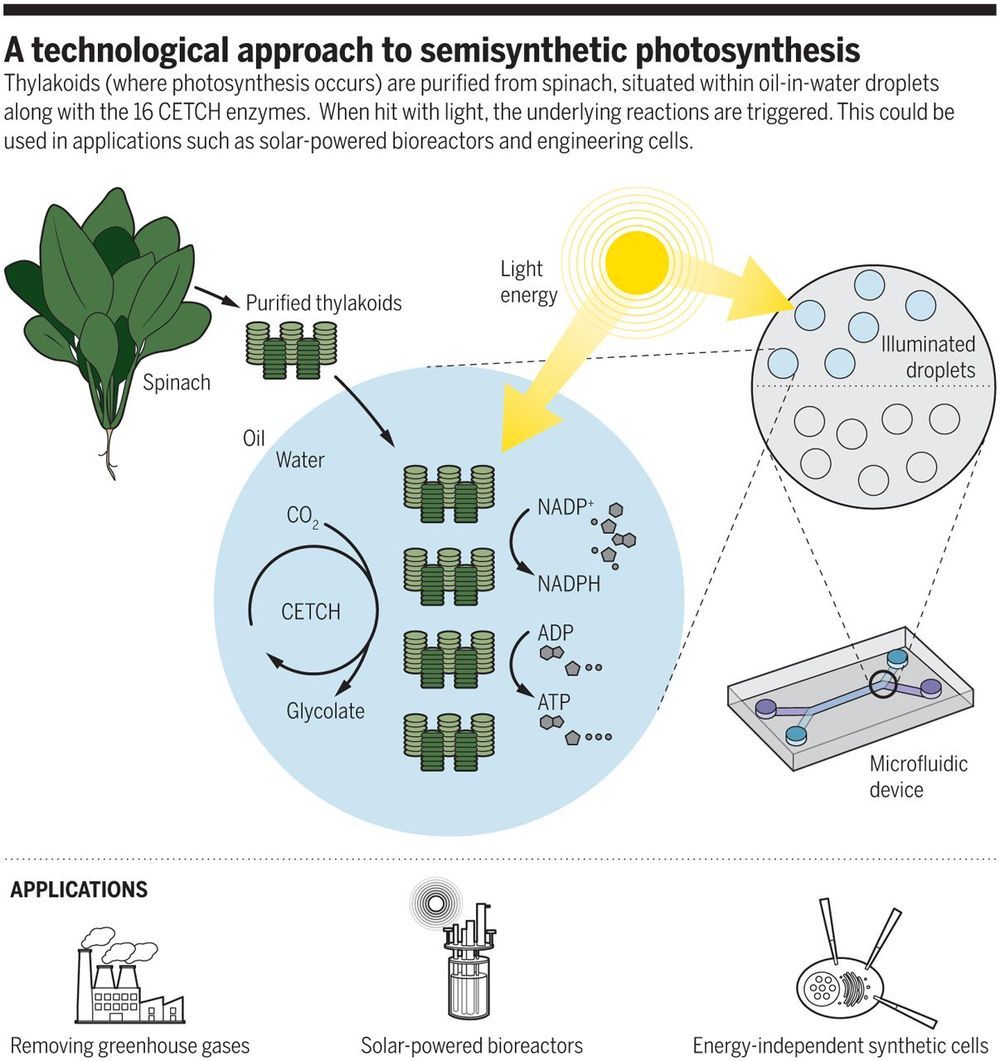
The creation of a fully artificial living cell would signify progress in both understanding current life and the development of synthetic organisms. A crucial component of any living organism is energy generation: the means to power its internal machinery. Because of their relative simplicity, catabolic reactions are the classical means for providing carbon and energy to synthetic cells, and much work has been done in optimizing which energy substrates work best for particular reactions ([ 1 ][1]). Despite robust success using small-molecule energy sources, the possibility of designing anabolic mechanisms that can harvest virtually limitless energy from light is very alluring yet remains unrealized.