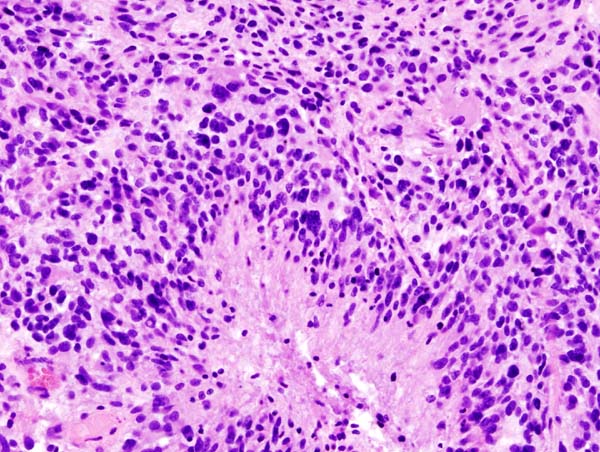
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have identified a tenacious subset of immune macrophages that thwart treatment of glioblastoma with anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade, elevating a new potential target for treating the almost uniformly lethal brain tumor.
Their findings, reported in Nature Medicine, identify macrophages that express high levels of CD73, a surface enzyme that’s a vital piece of an immunosuppressive molecular pathway. The strong presence of the CD73 macrophages was unique to glioblastoma among five tumor types analyzed by the researchers.
“By studying the immune microenvironments across tumor types, we’ve identified a rational combination therapy for glioblastoma,” says first author Sangeeta Goswami, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor of Genitourinary Medical Oncology.