New post!
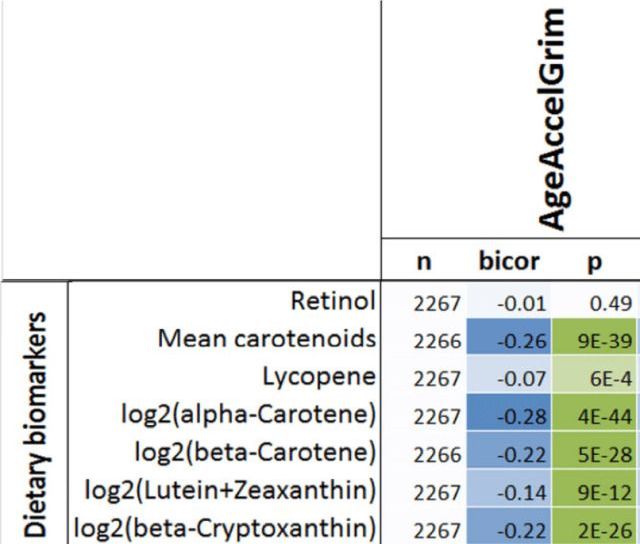
Having a faster rate of epigenetic aging, as measured by the epigenetic age metric, AgeAccelGrim, is associated with a significantly increased risk of death for all causes in a variety of cohorts, including the Framingham Heart Study (FHS), the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study, the InChianti study, the Jackson Heart Study (JHS), and collectively, when evaluated as a meta-analysis (Lu et al. 2019):
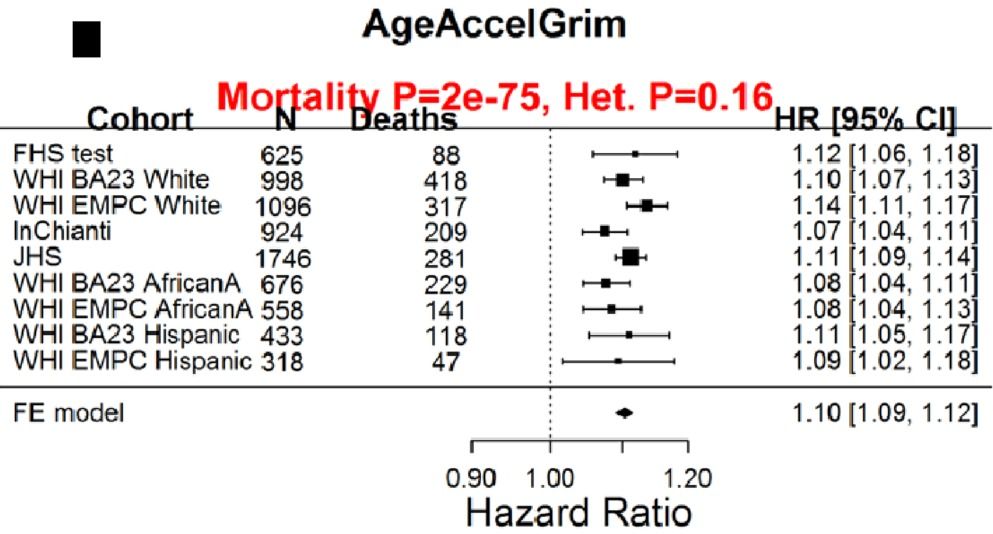
With the goal of minimizing disease risk and maximizing longevity, can epigenetic aging be slowed? Shown below is the correlation between dietary components with AgeAccelGrim. Dietary factors that were significantly associated (the column labelled, “p”) with a younger epigenetic age were carbohydrate intake, dairy, whole grains, fruit, and vegetables. In contrast, dietary fat intake and red meat were associated with older epigenetic ages (Lu et al. 2019):