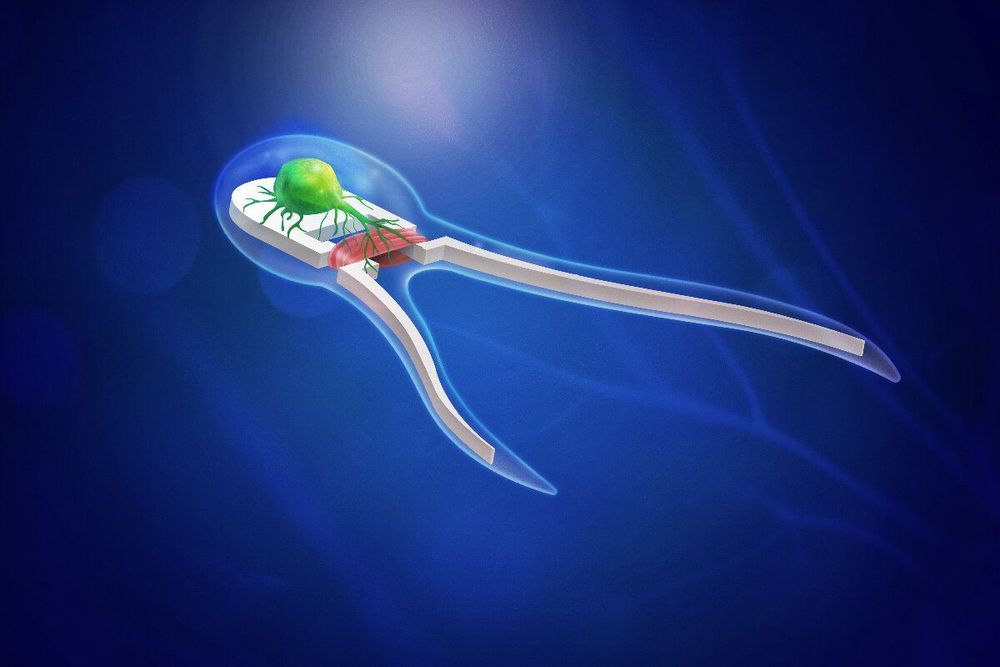
Researchers have developed soft robotic devices driven by neuromuscular tissue that triggers when stimulated by light—bringing mechanical engineering one step closer to developing autonomous biobots.
In 2014, research teams led by mechanical science and engineering professor Taher Saif and bioengineering professor Rashid Bashir at the University of Illinois worked together to developed the first self-propelled biohybrid swimming and walking biobots powered by beating cardiac muscle cells derived from rats.
“Our first swimmer study successfully demonstrated that the bots, modeled after sperm cells, could in fact swim,” Saif said. “That generation of singled-tailed bots utilized cardiac tissue that beats on its own, but they could not sense the environment or make any decisions.”