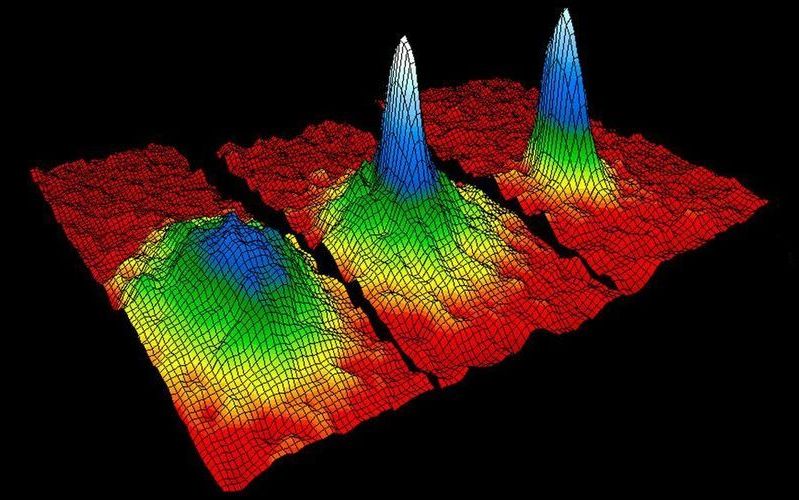
Before scientists discovered the new state of matter last week, we were basically all used to just three states of matter. After all, during our daily lives we encounter some variety of solids, liquids and gases. Solids hold a definite shape without a container, liquids conform to the shape of their container, and gases not only conform to a container, but also expand to fill it.
And there’s variety amidst these three: A crystalline solid, for example, has all its atoms lined up in exactly the precise order in perfect symmetry, while a quasicrystal solid fills all its space without the tightly regulated structure. Liquid crystals, which make up the visual components of most electronic displays, have elements of both liquids and crystal structures, as anyone who has ever pushed the screen of their calculator can confirm.
Under standard conditions on Earth, solids, liquids and gasses are the vast majority of what a person will experience in life. But that doesn’t mean there’s not a whole lot more beneath the surface.