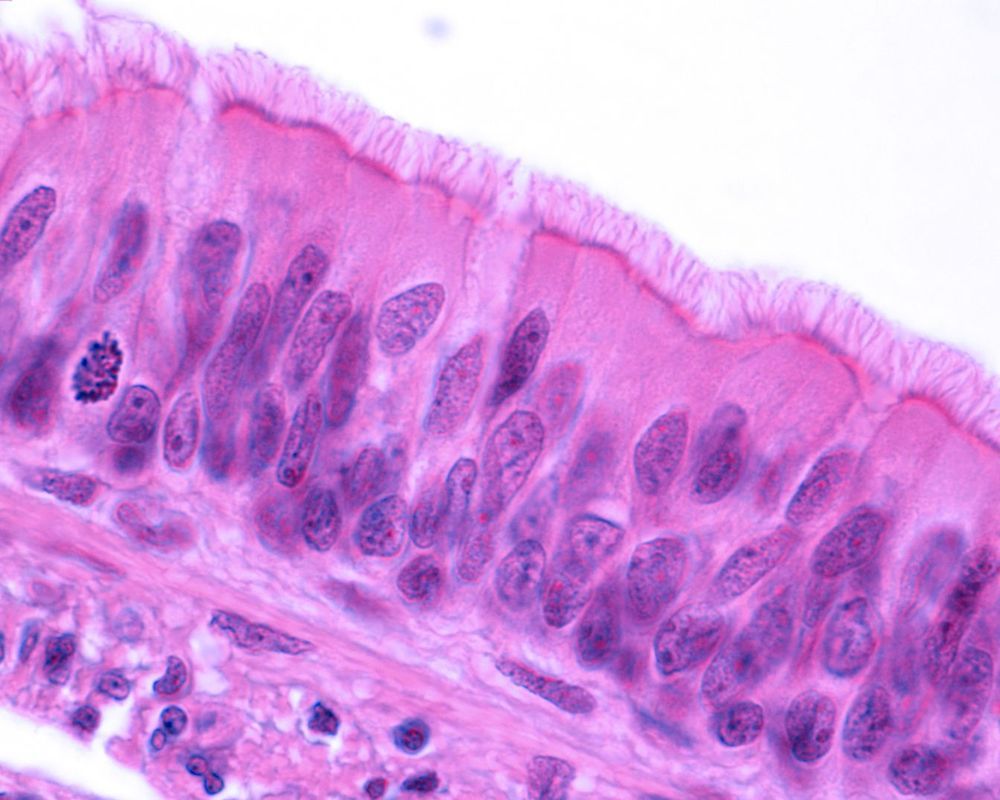
A research team led by the University of Cologne has identified the transcription factor Ets21c as a vital regulator of the regenerative system within the adult intestine of the fruit fly Drosophila. The study highlights the existence of trade-off mechanisms between stress resilience and longevity.
The intestinal epithelium is involved in nutrient absorption and digestion, but also serves as a selective barrier that prevents the intrusion of pathogens and toxic substances. The intestine is renewed over an organism’s lifetime through the function of stem cells that are capable of differentiating to maintain the tissue integrity and function.
On the other hand, stem cell malfunctions have been linked to tissue degeneration or cancer development. The research is shedding new light on the molecular basis of the regenerative processes under both favorable and stressful conditions.