It’s a remarkable story of recovery, but it’s unclear how useful this sort of therapy could become.
The background: Isabelle Holdaway had been given less than a 1% chance of survival after a lung transplant, carried out to combat the symptoms of cystic fibrosis, left her with an antibiotic-resistant infection. She had been sent home and was in a terrible physical condition: underweight, with liver failure, and with lesions on her skin from the infection.
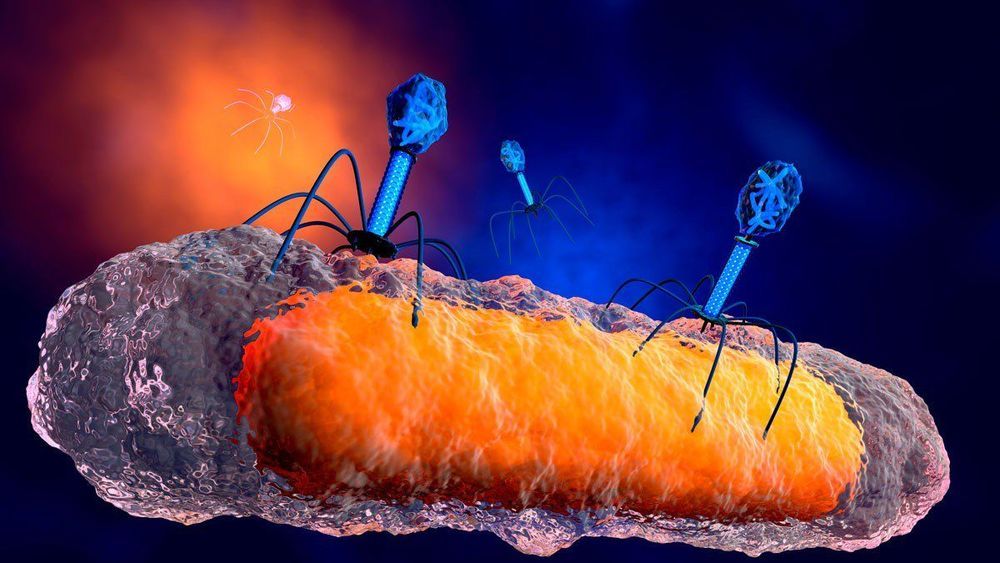
A breakthrough: Her consultant at Great Ormond Street Hospital in London worked with a team at the University of Pittsburgh to develop an untested phage therapy. This treatment used a cocktail of three phages, which are viruses that solely attack and kill bacteria. Two of the three phages, selected from a library of more more than 10,000 kept at the University of Pittsburgh, had been genetically engineered to be better at attacking the bacteria. The therapy was injected into her bloodstream twice daily and applied to the lesions on her skin, according to Nature Medicine.