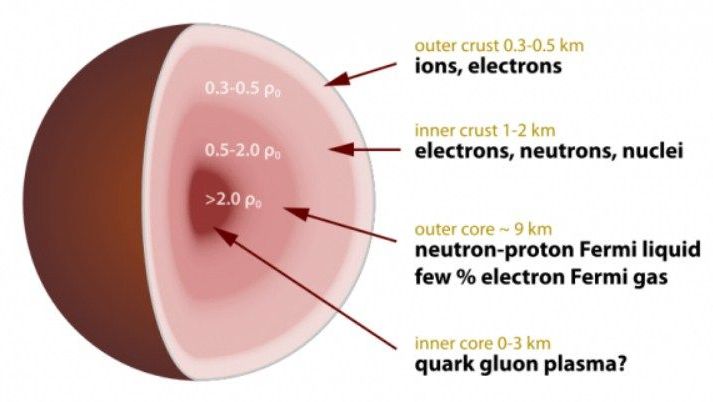
A neutron star is perhaps one of the most awe-inspiring and mysterious things in the Universe. Composed almost entirely of neutrons with no net electrical charge, they are the final phase in the life-cycle of a giant star, born of the fiery explosions known as supernovae. They are also the densest known objects in the universe, a fact which often results in them becoming a black hole if they undergo a change in masspace and science black hole is in space science
For some time, astronomers have been confounded by this process, never knowing where or when a neutron star might make this final transformation. But thanks to a recent study by a team of researchers from Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany, it may now be possible to determine the absolute maximum mass that is required for a neutron star to collapse, giving birth to a new black hole. space and science black hole is in space science
As with everything else relating to neutron stars, the process by which they become black holes has long been a source of fascination and bewilderment for astronomers. As the densest of all objects in the known universe, their mass cannot grow without bound – meaning that any increase in mass will also cause an increase in their density. space and science black hole is in space science.