Learning to deal with lignin is important for recycling and space settlements. Unused biomass on space settlements and long-term voyages is something that just can’t be tolerated. The same problem exists in dealing with plant waste on earth. A new process helps convert it into a precursor for polyester, which can be used for all kinds of other materials.
Plant cells are composed of three main substances: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. According to Yining Zeng, Michael E. Himmel, and Shi-You Ding in Biotechnology for Biofuels, the composition amounts to “40 to 50% of cellulose, 15 to 25% hemicelluloses, 20 to 25% lignin, and 5 to 10% other components.[1]” For the most part, the only truly useful part is the cellulose and the hemicellulose. The lignin is usually just thrown away. The most common use is fuel for heating units. That’s right. They just burn it.
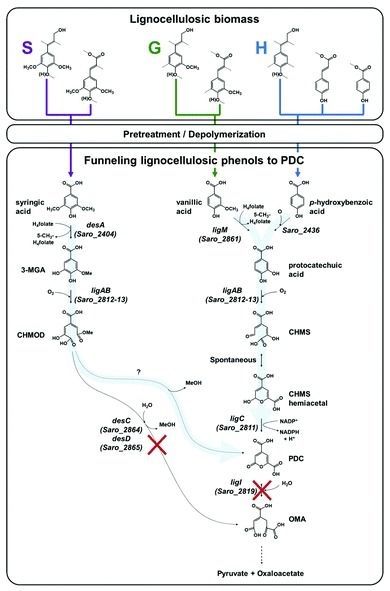
We can’t keep doing it that way. However, there really isn’t an alternative. Until now. A recent article in Science Daily referenced a new journal article about the use of Novosphingobium aromaticivorans. This is “genus of Gram-negative bacteria that includes N. taihuense, which can degrade aromatic compounds such as phenol, aniline, nitrobenzene and phenanthrene.[2]” Using genetic engineering, they deleted certain genes which allowed the microbe to convert lignin into 2-pyrone-4–6-dicarboxylic acid, which can be converted into polyester. The detailed information is available for free download and was published under the title “Funneling aromatic products of chemically depolymerized lignin into 2-pyrone-4–6-dicarboxylic acid with Novosphingobium aromaticivorans.[3]”