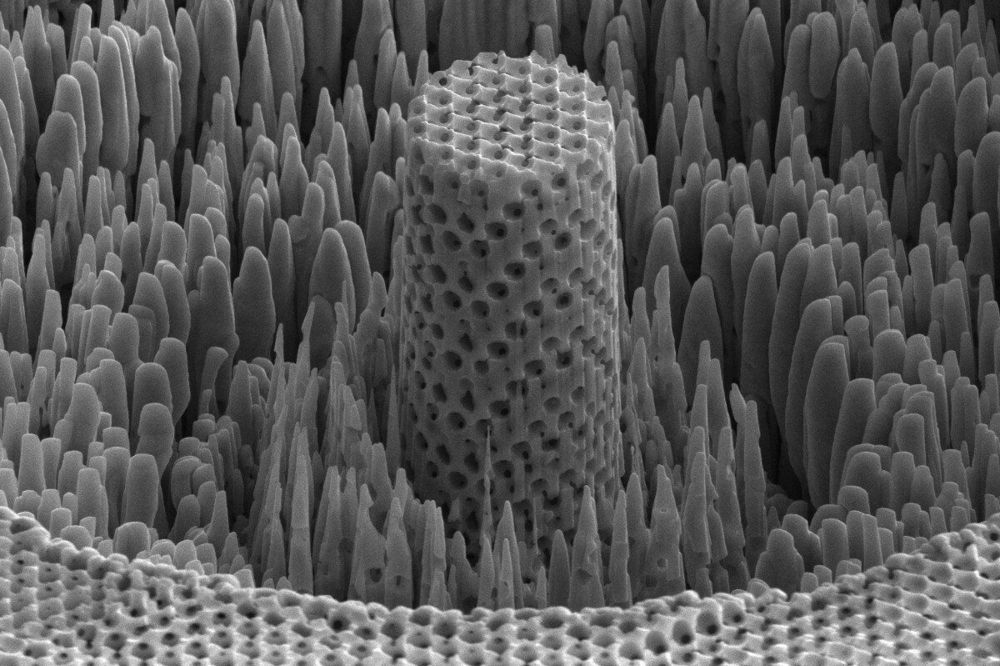
High-performance golf clubs and airplane wings are made out of titanium, which is as strong as steel but about twice as light. These properties depend on the way a metal’s atoms are stacked, but random defects that arise in the manufacturing process mean that these materials are only a fraction as strong as they could theoretically be. An architect, working on the scale of individual atoms, could design and build new materials that have even better strength-to-weight ratios.
In a new study published in Nature Scientific Reports, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania’s School of Engineering and Applied Science, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and the University of Cambridge have done just that. They have built a sheet of nickel with nanoscale pores that make it as strong as titanium but four to five times lighter.
The empty space of the pores, and the self-assembly process in which they’re made, make the porous metal akin to a natural material, such as wood.