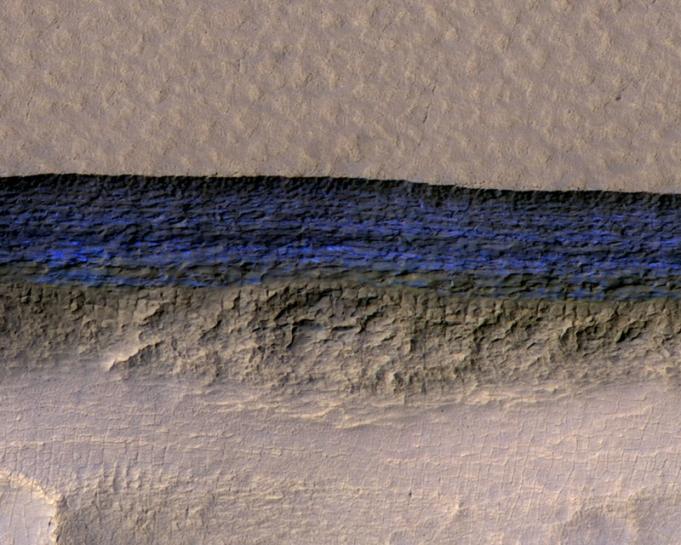
WASHINGTON (Reuters) — Scientists using images from an orbiting NASA spacecraft have detected eight sites where huge ice deposits near the Martian surface are exposed on steep slopes, a potential source of water that could help sustain future human outposts.
While scientists already knew that about a third of the surface of Mars contains shallow ground ice and that its poles harbor major ice deposits, the research published on Thursday described thick underground ice sheets exposed along slopes up to 100 yards (meters) tall at the planet’s middle latitudes.
“It was surprising to find ice exposed at the surface at these places. In the mid-latitudes, it’s normally covered by a blanket of dust or regolith,” loose bits of rock atop a layer of bedrock, said research geologist Colin Dundas of the U.S. Geological Survey’s Astrogeology Science Center in Flagstaff, Arizona, who led the study.
Read more