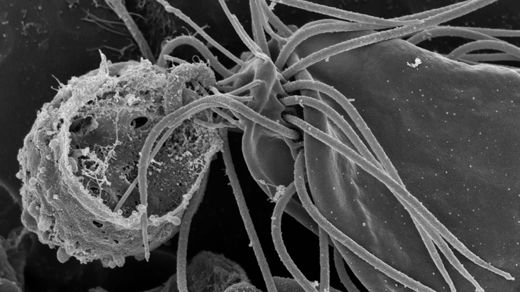
The tree of life just got another major branch. Researchers recently found a certain rare and mysterious microbe called a hemimastigote in a clump of Nova Scotian soil. Their subsequent analysis of its DNA revealed that it was neither animal, plant, fungus nor any recognized type of protozoan — that it in fact fell far outside any of the known large categories for classifying complex forms of life (eukaryotes). Instead, this flagella-waving oddball stands as the first member of its own “supra-kingdom” group, which probably peeled away from the other big branches of life at least a billion years ago.
“It’s the sort of result you hope to see once in a career,” said Alastair Simpson, a microbiologist at Dalhousie University who led the study.
Impressive as this finding about hemimastigotes is on its own, what matters more is that it’s just the latest (and most profound) of a quietly and steadily growing number of major taxonomic additions. Researchers keep uncovering not just new species or classes but entirely new kingdoms of life — raising questions about how they have stayed hidden for so long and how close we are to finding them all.