An international team of physicists and materials scientists from NUST MISIS, Bayerisches Geoinstitut (Germany), Linkoping University (Sweden), and the California Institute of Technology (U.S.) has discovered an “impossible” modification of silica-coesite-IV and coasite-V materials, which seems to defy the generally accepted rules for the formation of chemical bonds in inorganic materials formulated by Linus Pauling, who won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for that discovery. The research results were published in Nature Communications on November 15th, 2018.
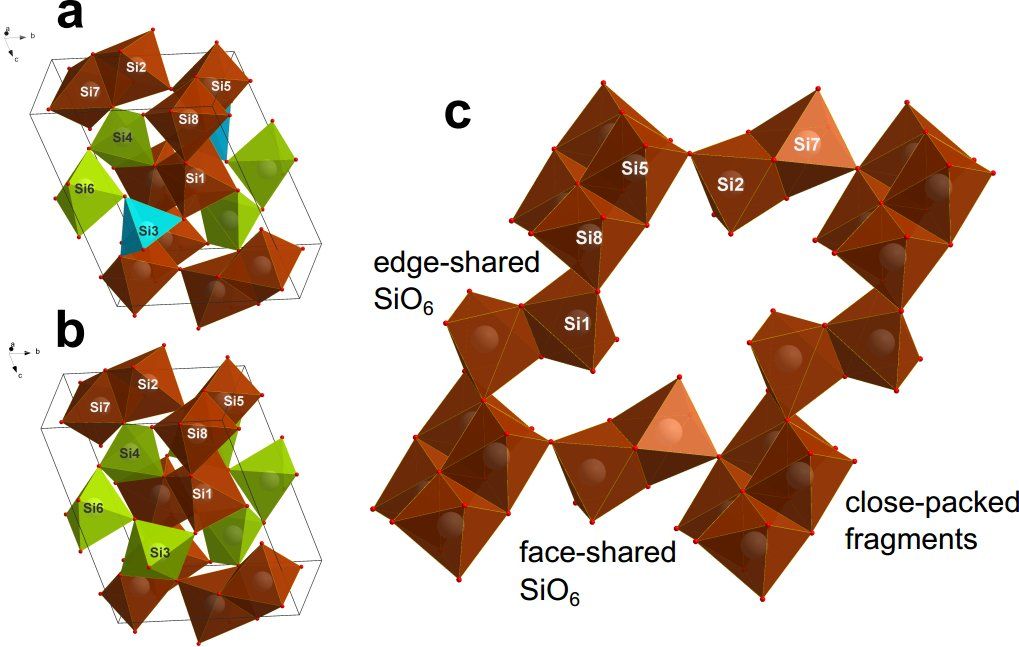
According to Pauling’s rules, the fragments of the atomic lattice in inorganic materials are connected by vertices, because bonding by faces is the most energy-intensive way to form a chemical connection. Therefore, it does not exist in nature. However, scientists have proved, both experimentally and theoretically, using NUST MISIS’ supercomputer, that it is possible to form such a connections if the materials are at ultra-high pressure conditions. The obtained results show that fundamentally new classes of materials exist at extreme conditions.
“In our work, we have synthesized and described metastable phases of high-pressure silica: coesite-IV and coesite-V. Their crystal structures are drastically different from any of the earlier described models,” says Igor Abrikosov, leader of the theoretical research team. “Two newly discovered coesites contain octahedrons SiO6, that, contrary to Pauling’s rule, are connected through common face, which is the most energy-intensive chemical connection. Our results show that the possible silicate magmas in the lower mantle of the Earth can have complex structures, which makes these magmas more compressible than predicted before.”
Read more