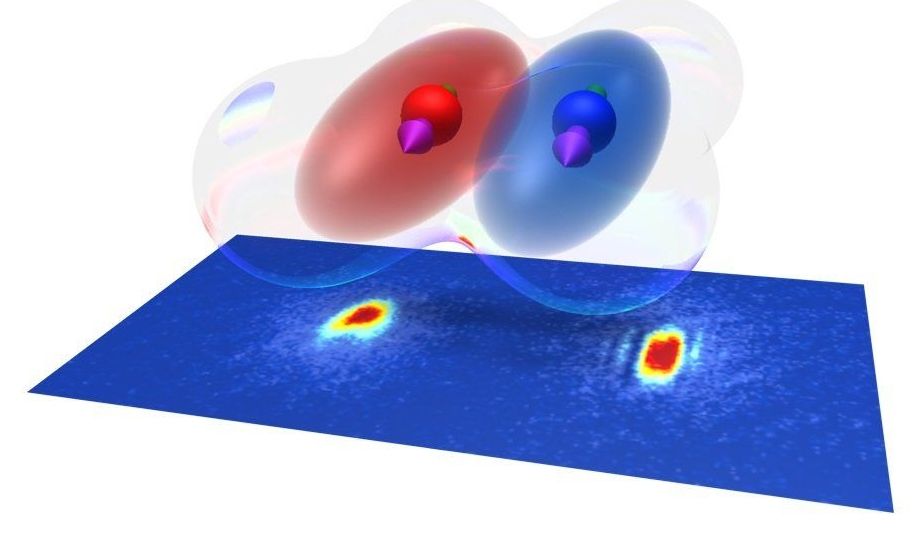
The experimental investigation of ultracold quantum matter makes it possible to study quantum mechanical phenomena that are otherwise inaccessible. A team led by the Innsbruck physicist Francesca Ferlaino has now mixed quantum gases of two strongly magnetic elements, erbium and dysprosium, and created a dipolar quantum mixture.
A few years ago, it seemed unfeasible to extend the techniques of atom manipulation and deep cooling in the ultracold regime to many-valence-electron atomic species. The reason is the increasing complexity in the atomic spectrum and the unknown scattering properties. However, a team of researchers, led by Ben Lev at Stanford University and an Austrian team directed by Francesca Ferlaino at the University of Innsbruck demonstrated quantum degeneracy of rare-earth species. Ferlaino’s group focused the research on erbium and developed a powerful, yet surprisingly simple approach to produce a Bose-Einstein condensate.
“We have shown how the complexity of atomic physics can open up new possibilities,” says Ferlaino. Magnetic species are an ideal platform to create dipolar quantum matter, in which particles interact with each other via a long-range and orientation dependent interaction as little quantum magnets.