Payback time.
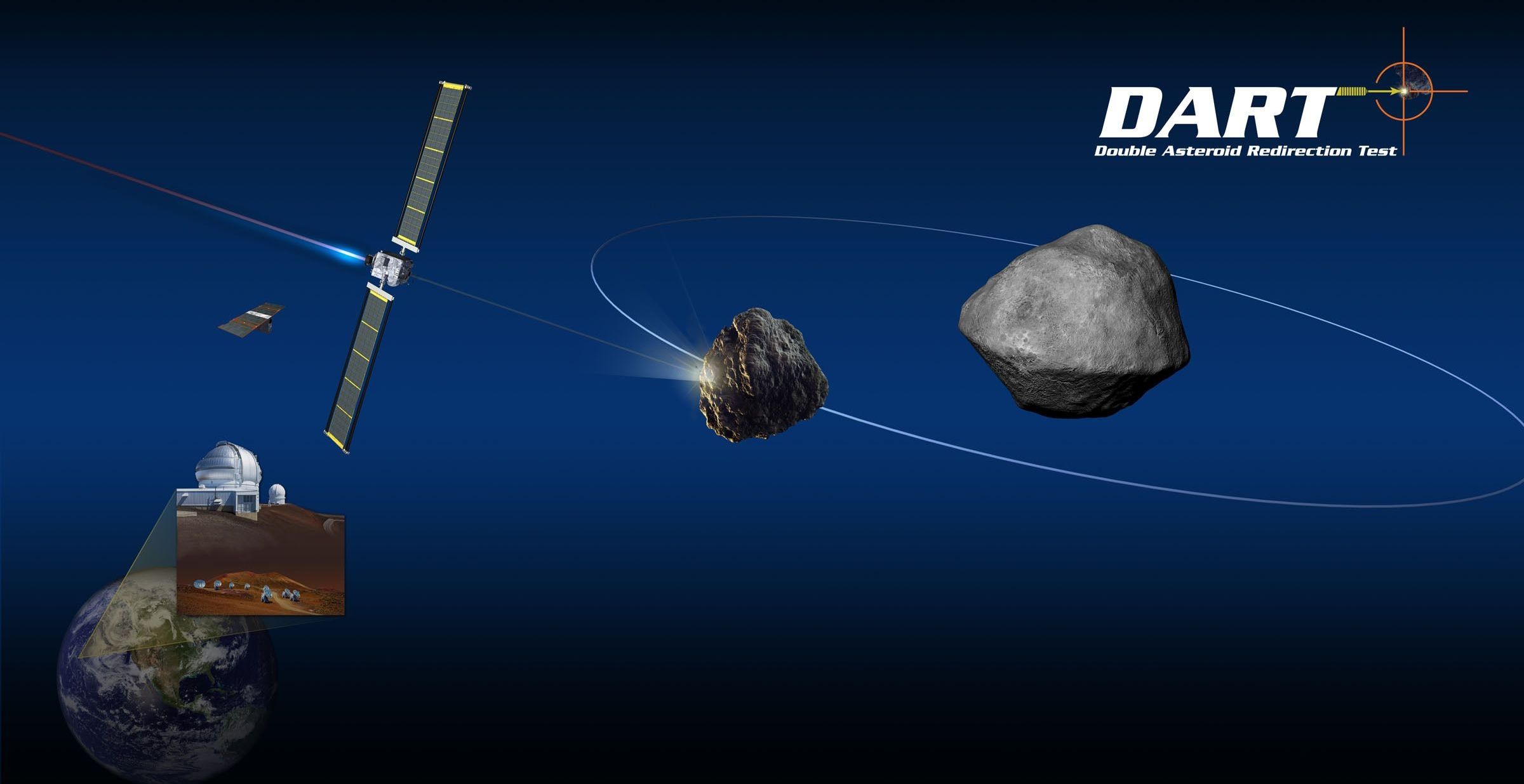
DART is a test of the kinetic impactor technique, a potential method to deflect an asteroid on course to impact the Earth. Kinetic impactors are one of only a small number of approaches we think are mature enough to deploy in the near future if they are needed (though we hope they won’t be). The most powerful asteroid-deflection technique is the use of a nuclear device. While such a device makes for good (and bad) sci-fi movies, there is widespread desire to develop alternate techniques.
The kinetic impactor concept is rather straightforward: ram the threatening object with a spacecraft and change its orbit so that it misses our planet. In theory, we could heave ever-larger masses at ever-faster speeds to deflect ever-larger objects. However, we think there is a practical limit — we don’t want to break up an incoming object into several pieces, lest we replace one big impact with multiple, only-slightly-smaller impacts. Exactly where that tradeoff lies is still uncertain, but we believe we can keep an object intact if we change its speed by less than the object’s own escape speed. In other words, since we think a lot of these objects are loose aggregates of gravel held together by gravity, we don’t want to shove so hard that we accidentally overcome that weak gravity and disperse the gravel.
For Ryugu, the asteroid being visited by the Japanese Hayabusa-2 sample return spacecraft right now, that maximum deflection speed is about 30 centimeters per second. That tells us two things: first, it’s important to find potential problem objects as soon as possible because the longer warning time we have, the less we need to change the object’s speed. Second, kinetic impactors would be used to make speed changes of millimeters to centimeters per second, so that’s the kind of speed change we need to be able to measure on a test flight.
Read more