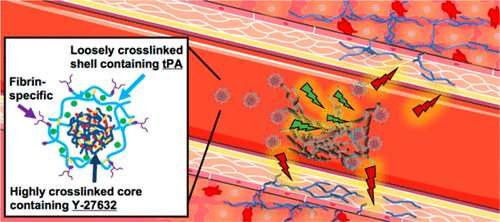
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have developed a drug-delivery system that allows rapid response to heart attacks without surgical intervention. In laboratory and animal testing, the system proved to be effective at dissolving clots, limiting long-term scarring to heart tissue and preserving more of the heart’s normal function.
“Our approach would allow health-care providers to begin treating heart attacks before a patient reaches a surgical suite, hopefully improving patient outcomes,” says Ashley Brown, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor in the Joint Biomedical Engineering Program (BME) at NC State and UNC. “And because we are able to target the blockage, we are able to use powerful drugs that may pose threats to other parts of the body; the targeting reduces the risk of unintended harms.”
Heart attacks, or myocardial infarctions, occur when a thrombus – or clot – blocks a blood vessel in the heart. In order to treat heart attacks, doctors often perform surgery to introduce a catheter to the blood vessel, allowing them to physically break up or remove the thrombus. But not all patients have quick access to surgical care.