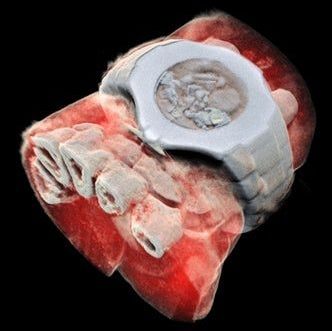
Medical X-ray scans have long been stuck in the black-and-white, silent-movie era. Sure, the contrast helps doctors spot breaks and fractures in bones, but more detail could help pinpoint other problems. Now, a company from New Zealand has developed a bioimaging scanner that can produce full color, three dimensional images of bones, lipids, and soft tissue, thanks to a sensor chip developed at CERN for use in the Large Hadron Collider.
Mars Bioimaging, the company behind the new scanner, describes the leap as similar to that of black-and-white to color photography. In traditional CT scans, X-rays are beamed through tissue and their intensity is measured on the other side. Since denser materials like bone attenuate (weaken the energy) of X-rays more than soft tissue does, their shape becomes clear as a flat, monochrome image.