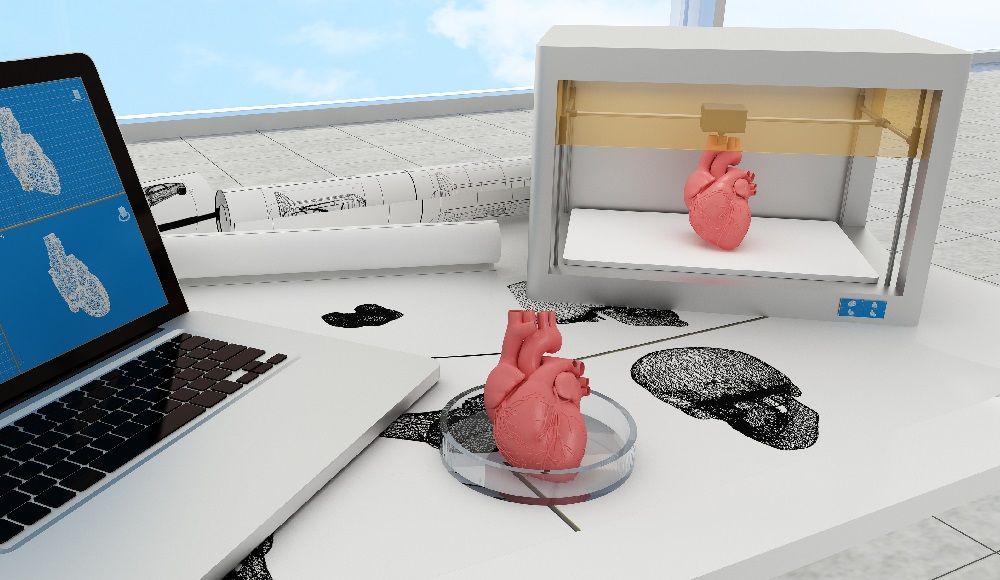
DIYers can bioprint living human organs by modifying an off-the-shelf 3D printer costing about $500, announce researchers who published the plans as open source, enabling anyone to build their own system. [This article first appeared on LongevityFacts. Author: Brady Hartman. ]
Scientists at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) developed a low-cost 3D bioprinter to print living tissue by modifying a standard desktop 3D printer and released the design as open source so that anyone can build their own system.
The biomedical engineering team led by Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) Associate Professor Adam Feinberg, Ph.D., BME postdoctoral fellow TJ Hinton, Ph.D. just published a paper in the journal HardwareX describing a low-cost 3D bioprinter. The article contains complete instructions for modifying nearly any commercial plastic printer, as well as printing and installing the syringe-based, large volume extruder.