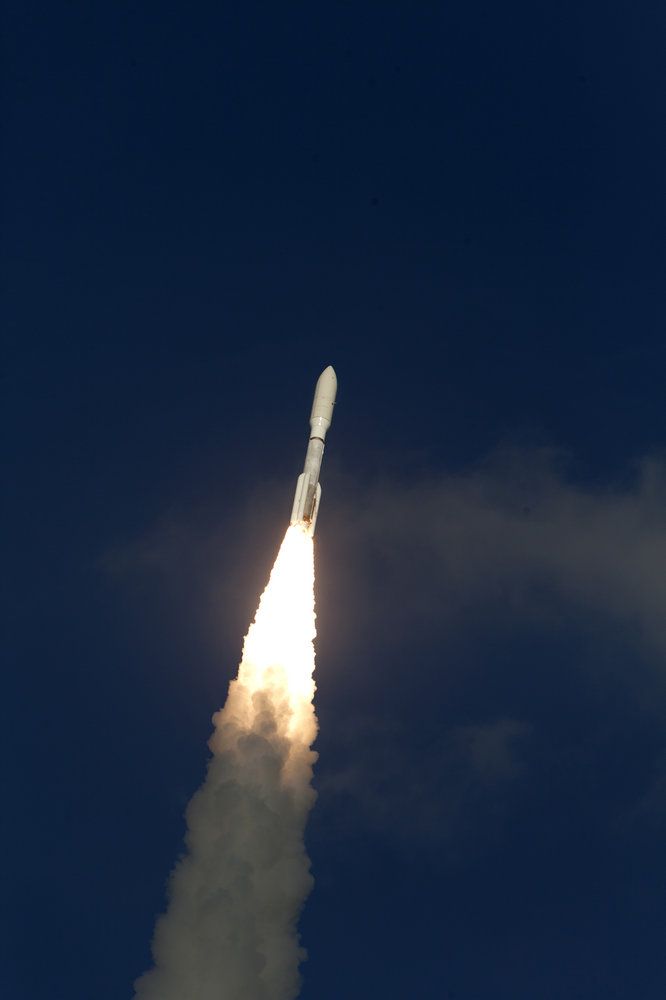
A powerful new weather satellite launched today (March 1) from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, heading toward a perch above the eastern Pacific Ocean to monitor extreme weather as it develops.
The satellite, called GOES-S (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S), lifted off on ULA’s Atlas V rocket at 5:02 p.m. EST (2202 GMT).
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) will operate GOES-S in partnership with NASA. The Lockheed Martin-built satellite will join GOES-East, currently in orbit, to provide a broad, high-definition view of weather on Earth. It is the second in a series of four advanced weather satellites that will reside in geostationary orbit — hanging in place over one spot on Earth as they orbit and the world turns. [GOES-S: NOAA’s Next-Gen Weather Satellite in Photos].