China has tasked 60,000 soldiers to increase the country’s total forest coverage in an attempt to combat its serious air pollution problem.



A couple of years ago, researchers at NASA’s Johnson Space Centre discovered a thruster system which actually generates thrust, despite requiring absolutely no propellant. The implications of this discovery are far-reaching; applications for space flight and other technologies which require propulsion could one day become far cheaper, allowing space exploration to expand exponentially.
The existence of this technology also further validates the fact that energy can be derived from tapping into the quantum vacuum, also known as “zero-point.”
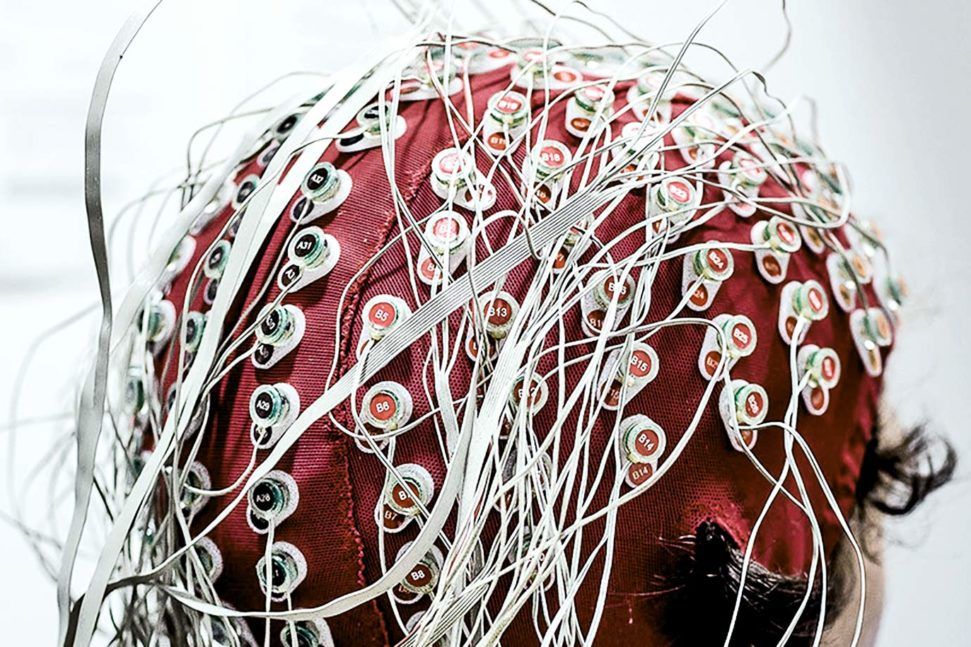

Researchers have identified a brain signal that indicates whether a person is comprehending what others are saying. The researchers have shown that they can track the signal using relatively inexpensive EEG (electroencephalography) readings taken on a person’s scalp.
During everyday interactions, people routinely speak at rates of 120 to 200 words per minute. For a listener to understand speech at these rates—and not lose track of the conversation—the brain must comprehend the meaning of each of these words very rapidly.
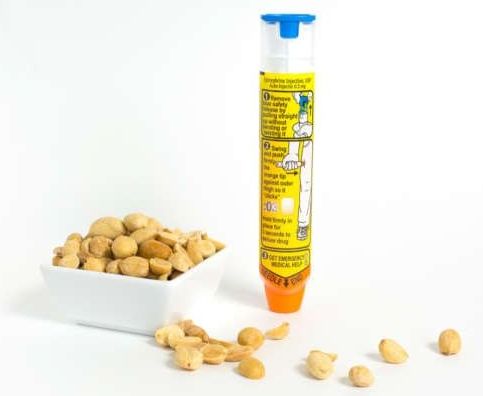
Imagine constantly worrying that something you eat is going to cause your throat to swell shut or your heart to stop beating. That’s the reality people with severe peanut allergies must live with every day, because their bodies launch out-of-control immune responses against even a trace of peanut protein.
But now, relief may be on the horizon. A phase 3 clinical trial by pharmaceutical company Aimmune Therapeutics shows that gradual and methodical exposure to purified peanut protein can train the body to drastically tone down the reaction. After one year of daily treatment with the company’s peanut protein-filled capsules, currently called AR101, study participants could safely tolerate 30 times more allergen than they could before the trial began.
The trial included 496 children aged 4 to 17 with allergies so severe that they could not ingest more than 30 milligrams of peanut protein without experiencing moderate to highly dangerous effects. For reference, one peanut contains 250 to 350 milligrams of peanut protein.
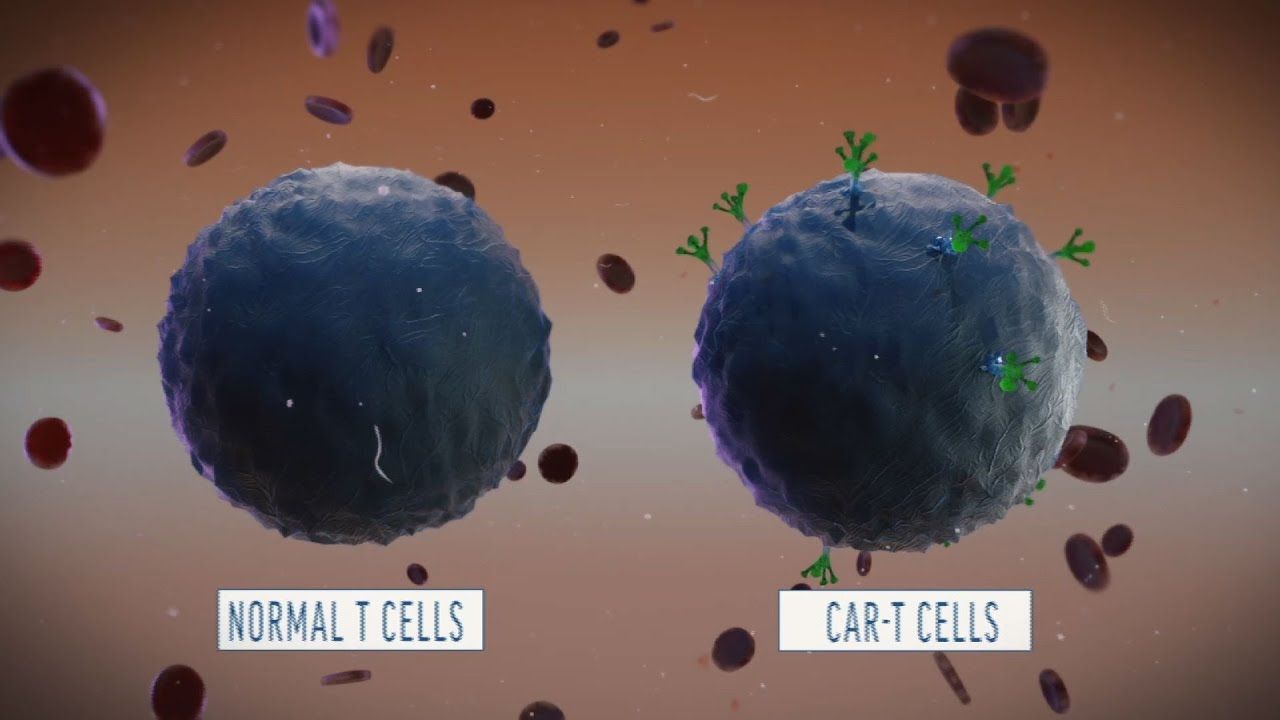
According to China’s National Central Cancer Registry, Esophageal cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in China. Like many other types, cancer of the esophagus can be treated with chemotherapy. But, as is also true of other forms of cancer, chemotherapy isn’t always successful. In China, and around the world, there’s a great need for the development of new treatments.
Dr. Shixiu Wu, president of the Hangzhou Cancer Hospital, has tested a somewhat new treatment that takes a patient’s T-cells from the body, genetically edits them to target cancerous cells, then puts the altered cells back. If the process sounds at all familiar, it’s probably because using T-cells in this manner was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration back in August 2017.
We reported on a pair of CAR-T studies in December that used T-cells to fight cancer, as will the first CRISPR trial set to take place in the United States.


Using artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques, researchers at Shiley Eye Institute at UC San Diego Health and University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues in China, Germany and Texas, have developed a new computational tool to screen patients with common but blinding retinal diseases, potentially speeding diagnoses and treatment.

