Nectome will preserve your brain, but you have to be euthanized first.
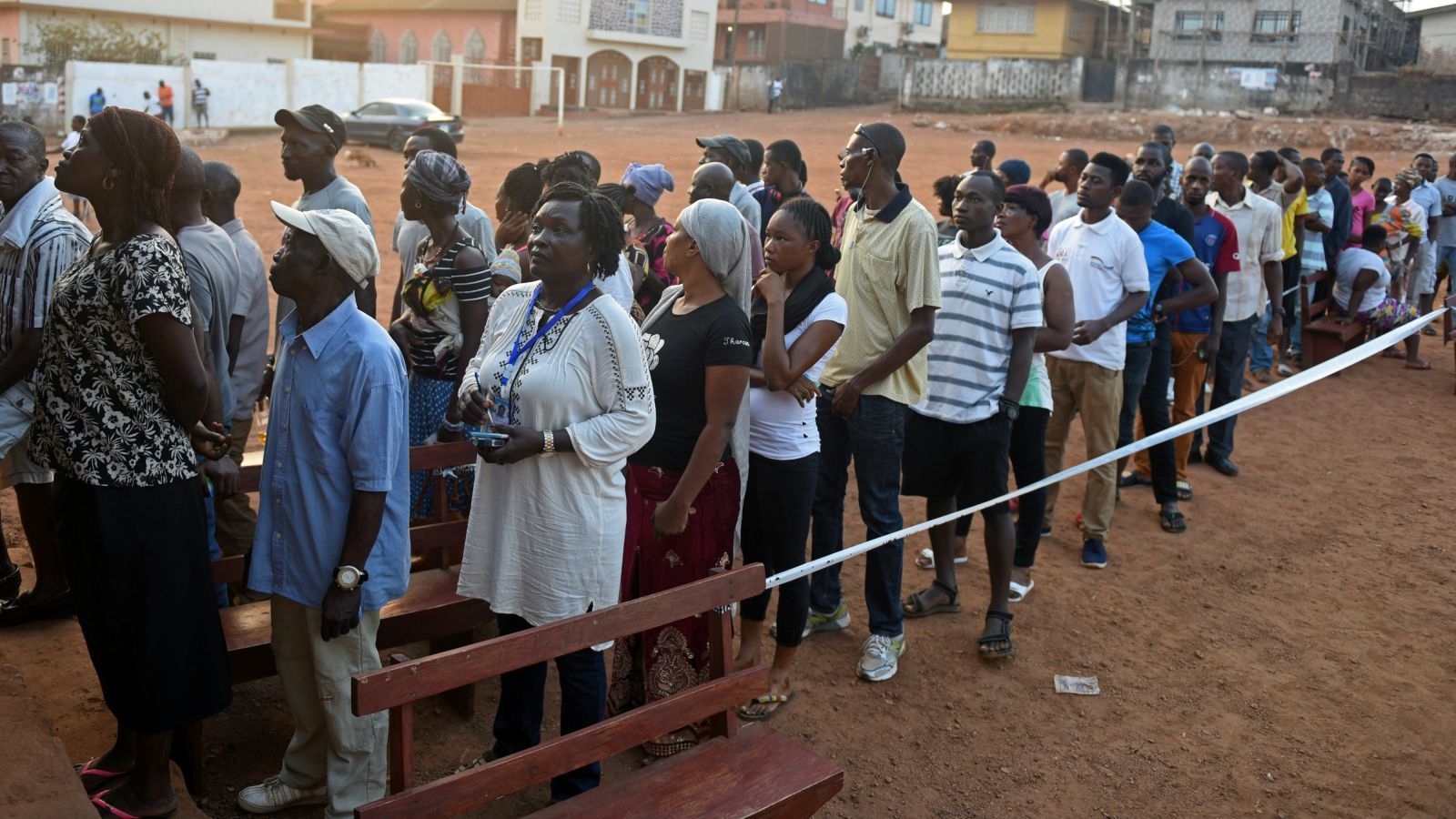



On Mar. 7, elections in Sierra Leone marked a global landmark: the world’s first ever blockchain-powered presidential elections.
As president Ernest Bai Koroma leaves office after serving two five-year terms, the maximum allowed constitutionally, Sierra Leoneans have had to pick from a pool of 16 candidates including the ruling party’s Samura Kamara, the erstwhile foreign minister, and Julius Maada Bio, former military head of state and candidate of the main opposition party.
Results released by Sierra Leone’s election commission (NEC) suggest a run-off between Bio and Kamara is likely with neither candidate securing the required 55% of votes so far. Sierra Leone’s new president will be tasked with a continued rebuilding given the country’s recent major disasters. In 2014, an Ebola outbreak led to nearly 4,000 deaths and GDP losses estimated at $1.4 billion—a major loss for one of the world’s poorest countries. Last year Sierra Leone’s capital also suffered devastating flooding and mudslides believed to have claimed more than 1,000 lives.
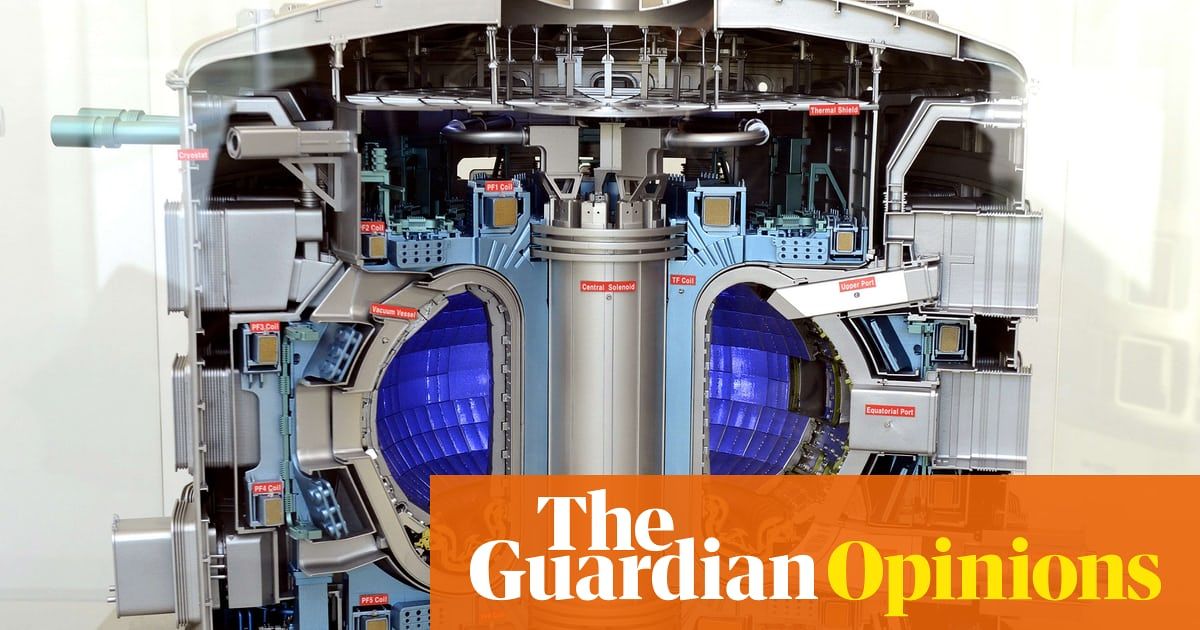

Fusion technology promises an inexhaustible supply of clean, safe power. If it all sounds too good to be true, that’s because it is. For decades scientists struggled to recreate a working sun in their laboratories – little surprise perhaps as they were attempting to fuse atomic nuclei in a superheated soup. Commercial fusion remains a dream. Yet in recent years the impossible became merely improbable and then, it felt almost overnight, technically feasible. For the last decade there has been a flurry of interest –and not a little incredulity –about claims, often made by companies backed by billionaires and run by bold physicists, that market-ready fusion reactors were just around the corner.
Until recently the attractions and drawbacks of nuclear fusion reactors were largely theoretical. Within a decade this will not be the case.
Mon 12 Mar 2018 14.24 EDT Last modified on Mon 12 Mar 2018 19.15 EDT.
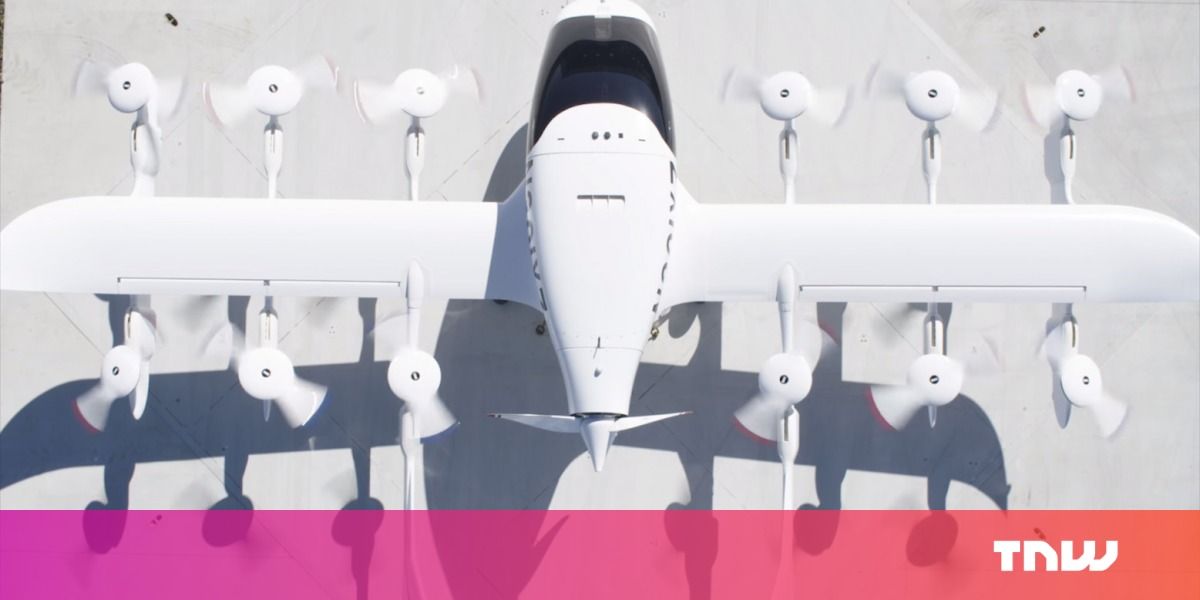

Kitty Hawk, an aeronautics firm funded by Alphabet CEO and Google co-founder Larry Page, is inching closer to its plans of creating Uber for flights: it’s unveiled Cora, a fully electric self-flying air taxi that can cover 100 km (62 miles) on a single charge – and you’ll soon be able to hail one with your phone.
Cora has been in the works for a while now, and it’s just been cleared to begin tests in New Zealand. The goal is for Kitty Hawk to launch a fleet of its flying taxis within the next three years. You can Click on photo to start video.
” target=“_blank” rel=“nofollow noopener”>watch a clip of the vehicle in action here.
Powered by batteries and driven by a dozen rotors, the vehicle has a wingspan of 3.6m (12 feet), and can seat two passengers. It can take off vertically, which means it doesn’t need a runaway to land on – a parking lot or rooftop will do. Kitty Hawk is already managing operations in New Zealand through Zephyr Airworks, a company it set up in the country in 2016, and is also building an app that will let you hail flights.
An article I wrote:
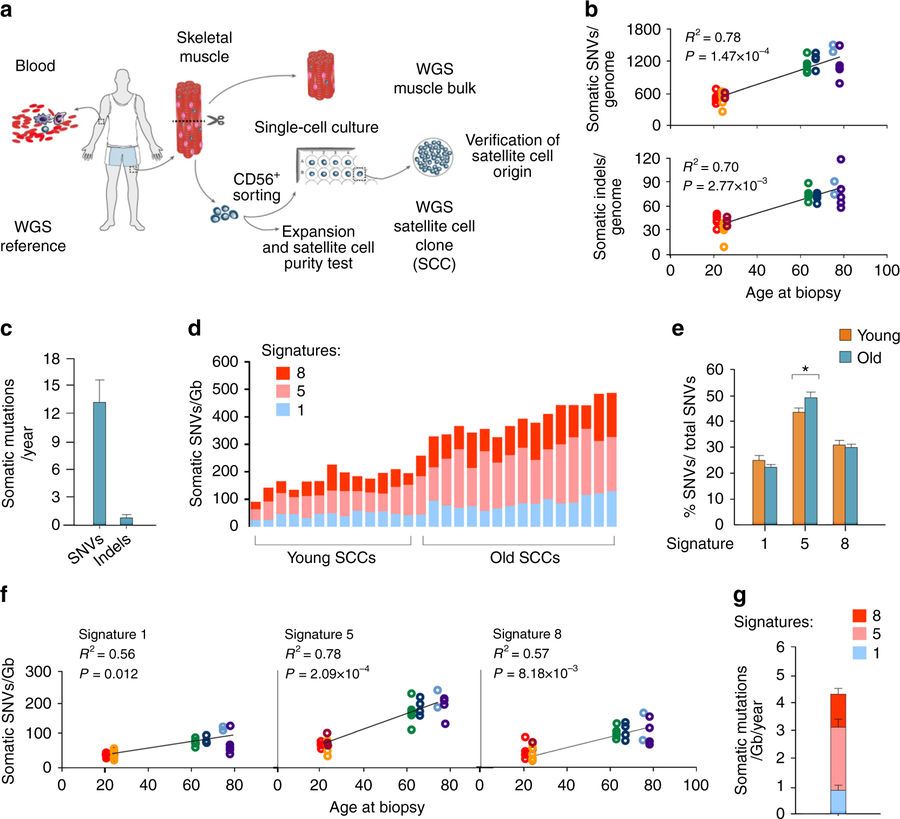
Study based upon human skeletal muscle aging, mutagenesis, and the role of #satellite cells
“A more comprehensive understanding of the interplay of stem cell–intrinsic and extrinsic factors will set the stage for improving cell therapies capable of restoring tissue homeostasis and enhancing muscle repair in the aged.”
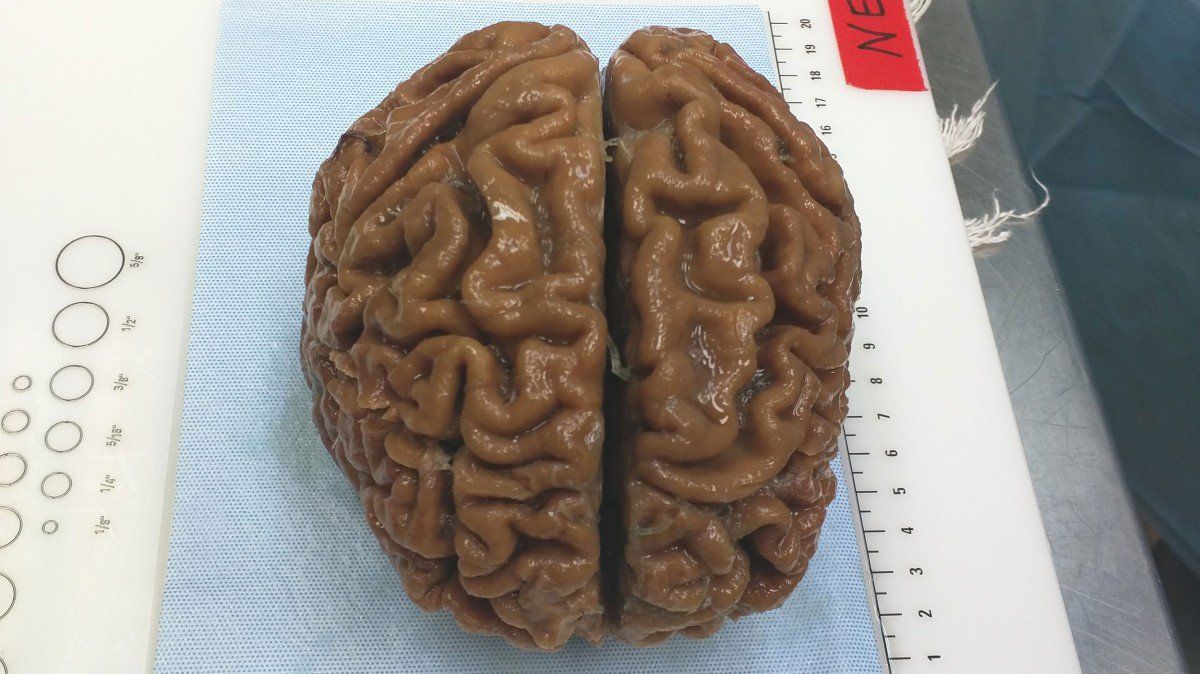
Human aging has multiple effects on the human body. One of the effects of human aging is the reduction in skeletal muscle (SkM) function and a reduction in the number and activity of satellite cells (SCs), the resident stem cells. The whole genome of single SC clones of the leg muscle vastus lateralis from healthy individuals of different ages (21–78 years) was analyzed, to study the specific connection between SC aging and muscle impairment. In healthy adult muscle rapid increase of SCs is consistent with the accumulation rate of 13 somatic mutations per genome per year. Mutations typically do not happen in SkM-expressed genes because they are protected. However, as mutations in exons and promoters increase, genes involved in SC activity and muscle function are targeted which results in aging. Exons are coding sections of an RNA transcript, or the DNA encoding it, that are translated into protein. Proteins are the synthesis of molecules.
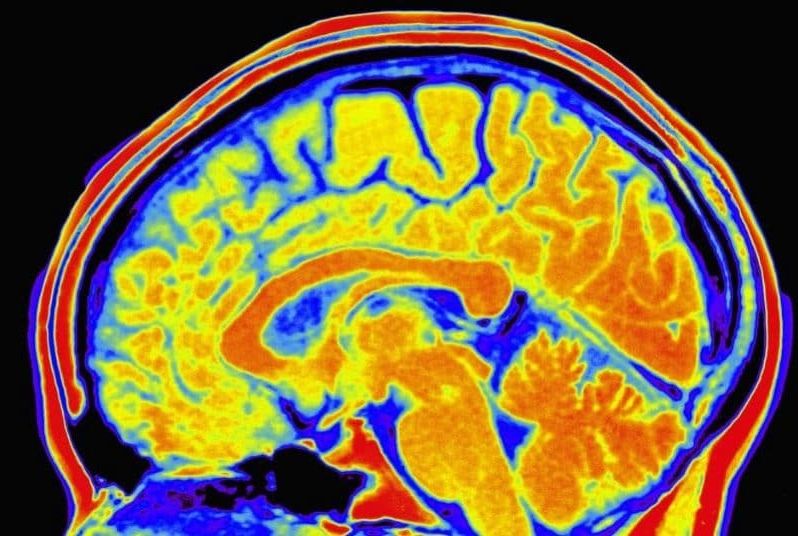
I ntelligence could be measured with a swab of saliva, or drop of blood, after scientists showed for the first time that a person’s IQ can be predicted just by studying their DNA.
In the largest ever study looking at the genetic basis for intelligence, researchers at the University of Edinburgh and Harvard University discovered hundreds of new genes linked to brain power.
Previous studies have suggested that between 50 per cent and 75 per cent of intelligence is inherited, and the rest comes through upbringing, friendship groups and education. That figure was calculated by studying identical twins who share the same DNA, therefore any differences in IQ between them must be non-genetic.
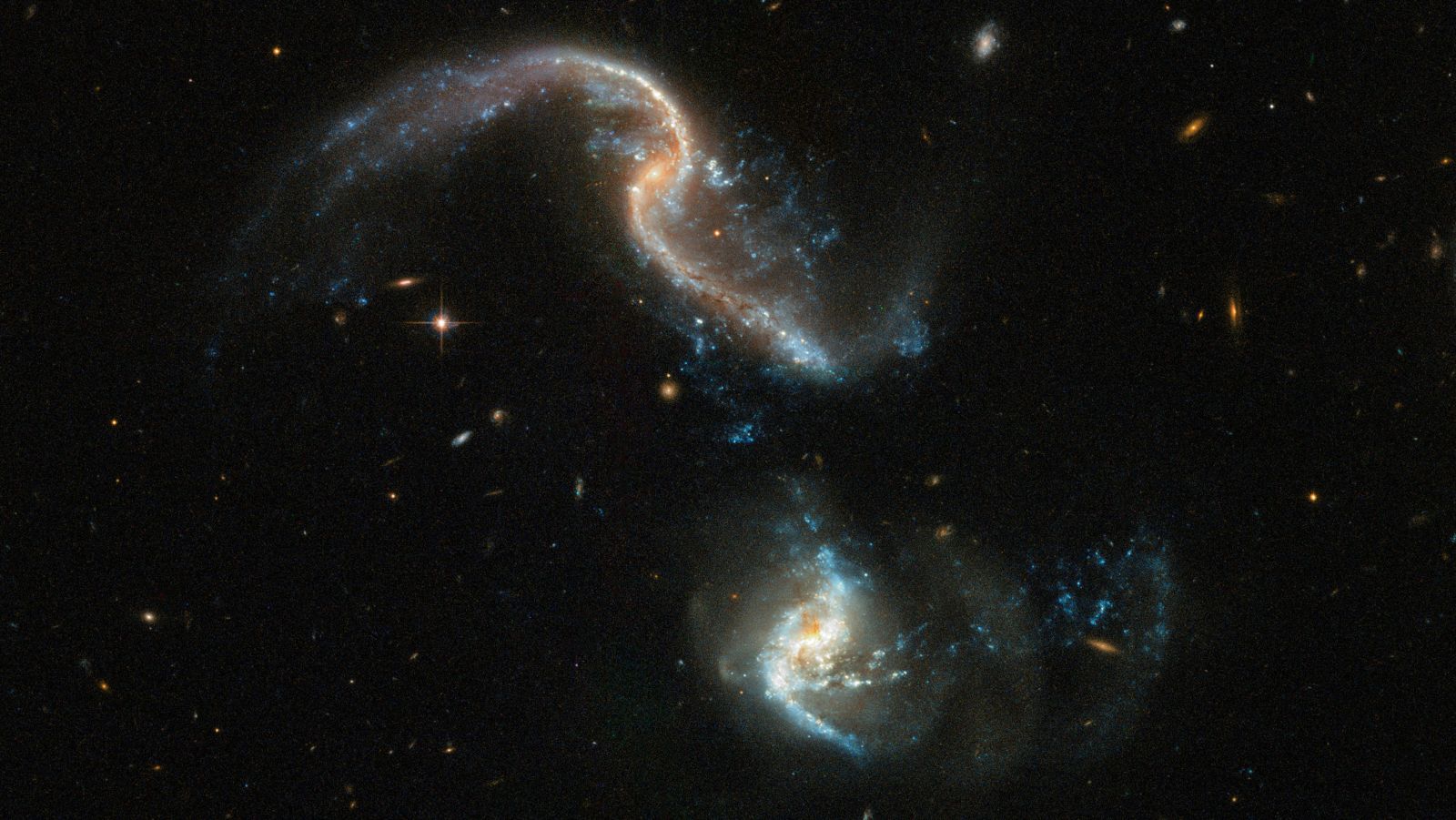


Located 350 million light-years away, two neighbor galaxies are slowly being brought together by gravitational forces.
The Hubble Space Telescope captured the pair’s beautiful cosmic dance in a recent photo of the spiral galaxies, known as Arp 256.
One of the most stunning aspects of the image are the swaths of blue on the outer edges of both galaxies. Those are “stellar nurseries,” collections of gas and dust in the process of becoming new stars. Stellar nurseries are set off by intense gravitational forces, like the massive forces of two galaxies slowly merging.