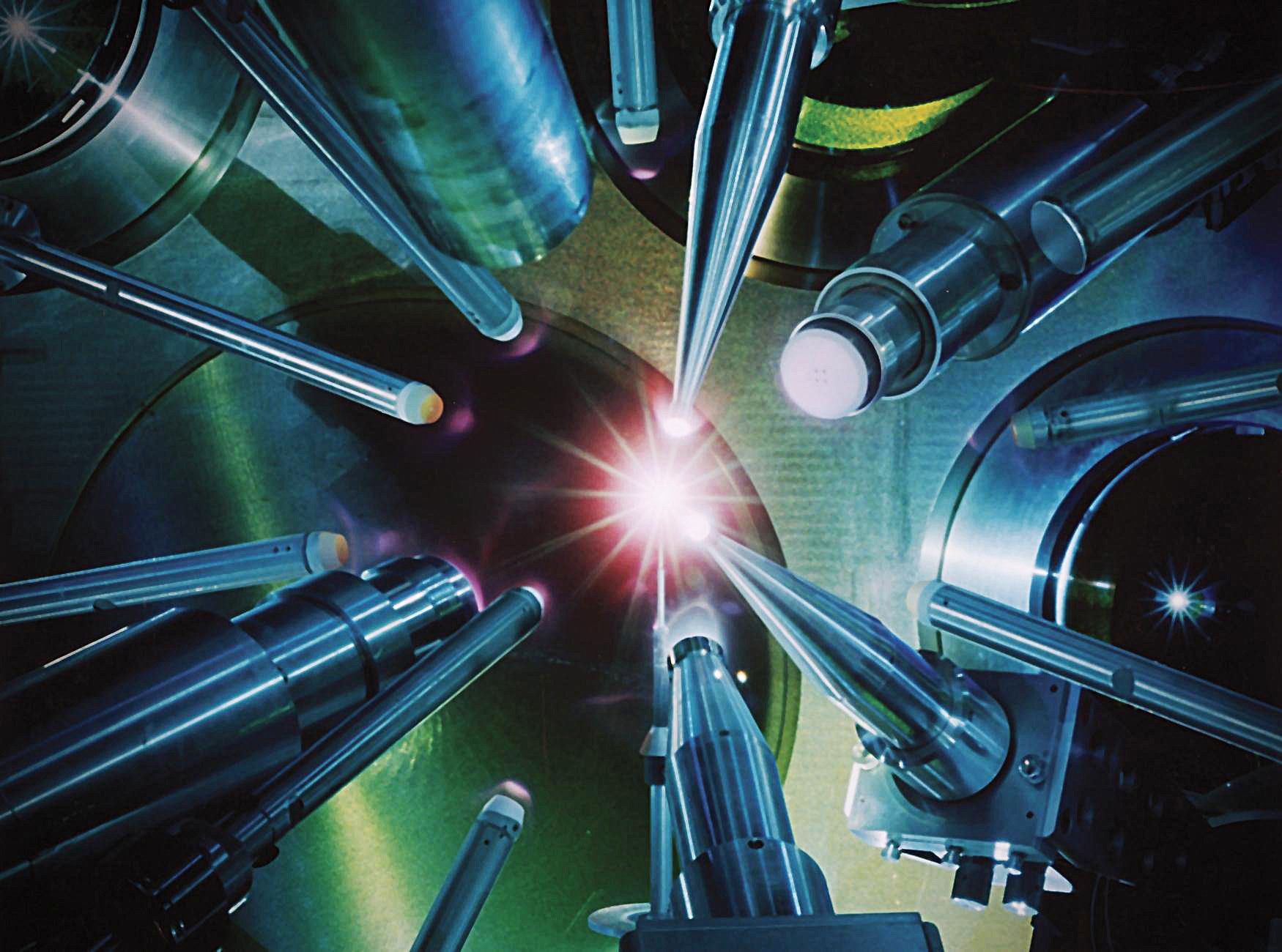
The development of ultra-intense lasers delivering the same power as the entire U.S. power grid has enabled the study of cosmic phenomena such as supernovae and black holes in earthbound laboratories. Now, a new method developed by computational astrophysicists at the University of Chicago allows scientists to analyze a key characteristic of these events: their powerful and complex magnetic fields.
In the field of high-energy density physics, or HEDP, scientists study a wide range of astrophysical objects—stars, supermassive black holes at the center of galaxies and galaxy clusters—with laboratory experiments as small as a penny and lasting only a few billionths of a second. By focusing powerful lasers on a carefully designed target, researchers can produce plasmas that reproduce conditions observed by astronomers in our sun and distant galaxies.
Planning these complex and expensive experiments requires large-scale, high-fidelity computer simulation beforehand. Since 2012, the Flash Center for Computational Science of the Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics at UChicago has provided the leading open computer code, called FLASH, for these HEDP simulations, enabling researchers to fine-tune experiments and develop analysis methods before execution at sites such as the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory or the OMEGA Laser Facility in Rochester, N.Y.